Author Archive
Following is an excerpt from a PTI report in Hindu Business Line.
At least three more Apparel Training and Design Centres (ATDC) will be set up in Orissa. The proposed centers will be set up jointly by the Apparel Export Promotion Council (APEC) under union ministry of textiles and state government at Baripada, Cuttack and Sambalpur very soon.
…according to handlooms and textile secretary, Ms Arati Ahuja.
The APEC is now running three ATDCs at Bhubaneswr, Berhampur and Rourkeal with 100 per cent placement guarantee.
… Almost all the students who passed out from the Bhubaneswar centre have got placement, said Ms Lopamudra Das, head of the Bhubaneswar center.
The placement was made in reputed garment companies, she said.
In a related news in Expressbuzz, the recently established Indian Institute of Handloom Technology at Baragarh seems to be going through teething problems. Following is an excerpt.
… The IIHT was established here after much struggle last year as there was an inordinate delay in identifying and handing over the land for the institute. As work on the required infrastructure is far from over, it is now being mooted to hold the final year classes for the IIHT course at Salem. Ever since its inception, the IIHT has been operating on Panchayat College premises here.
As required by the IIHT officials, the institute was provided with classrooms, hostel for students besides four staff quarters. It was hoped that the infrastructure would be readied soon and the institute would be shifted to its new premises at Bhatli Road. But more than a year has passed and only a boundary wall has come up.
… Meanwhile, District Collector Suresh Prasad Padhy has apprised the Secretary, Higher Education of the slow pace of work at IIHT which is likely to be completed by 2013. …
November 10th, 2009
Thanks to Kanhu Roul for the pointer. The following is an excerpt from http://www.mbauniverse.com/aspirantinn.php?id=2534.
The Birla Institute of Management Technology (BIMTECH) held its 21st Annual Convocation on Saturday, November 7, 2009 at the Greater Noida campus of the MBA institute. The Chief Guest was the former President of India, Bharat Ratna Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam.
The Convocation ceremony started with the welcome address by Jayashree Mohta, Chairperson, Board of Governors, BIMTECH.
Speaking on the occasion, Dr. Harivansh Chaturvedi, Director, BIMTECH, informed that the institute is planning to open new campuses in Bhubaneswar, Orissa and Sonepat, Haryana.
Said Dr Chaturvedi, “I am glad to report that we have been invited by two state governments, Haryana and Orissa to open campuses in their states. BIMTECH has been recently allotted 29 acres of land at Bhubaneswar, Orissa and 7.5 acres at Sonepat, Haryana.” …
BIMTECH is decently ranked among private management institutes. I think this is different from the BITS Pilani group which planned to establish an IIM type institute and both Orissa government and AP government had pursued it. Orissa was also pursuing a BITS Pilani campus. I don’t know what happened to that. Two years back when we and the CM contacted Sir KK Birla about it we received individual responses which suggested that we wait till BITS-Pilani Hyderabad is operational. Now that BITS-Pilani Hyderabad is operational, I think it is time to broach the topic again with the right people. (Sir Birla has since then gone to the heavenly abode and since then Mr. Kumar Mangalam Birla is in charge of BITS Pilani.)
November 10th, 2009
Following is from http://www.ficci.com/events/20009/ISP/richard.pdf.
Minister SibaI, Mr. Singhani, Mr. Mittal, Dr. Mitra, distinguished guests:
It is a great pleasure to be with you this morning, and an honor to have the opportunity to address this distinguished audience, filled as it is with a diverse and accomplished group of leaders from across India. I thank you for the opportunity.
Over the next two days, you will hear about many of the most pressing issues facing higher education in India, issues that are also challenging universities in the United States and across the globe: reforming regulation and accreditation; using technology; ensuring afford ability; and promoting publicprivate cooperation. All of these issues present opportunities to improve our universities and further the good work they do in society.
It is an honor to have with us today the Union Minister for Human Resource Development, Kapil Sibal.
Only a week ago, Minister Sibal visited Yale, and I was pleased to learn about his ambitious vision for higher education in India. He has shown intrepid leadership in fashioning the Ministry’s plans for new world-class universities, and for making the challenge of improving India’s higher education system a national priority.
There is no doubt that India possesses a number of educational institutions that have made their mark, and will continue to make their mark, on the world stage. The Indian Institutes of Technology, the Indian Institute of Science, and the Indian Institutes of Management are among these. But the rise of this country to become one of world’s economic powerhouses begs for expansion in India’s higher education system. The need is a striking one. India is already the world’s largest democracy. In two decades, it will be the most populated country in the planet, and by 2050, it is likely to become the second largest economy in the world.
We hear much about today’s "knowledge economy,” and for good reason: it is the innovation born at the world’s great universities – and the leaders who are trained there – that will drive the economic growth and continued prosperity of India and the world’s other leading economies in the coming decades.
With this in mind, Minister Sibal and the Indian government have rightly set the dual goals of increasing access to higher education and creating a group of new, worldclass universities. Today, only 12 percent of college-age Indian students pursue higher education. By contrast, in the United States, 63 percent of students go to college; among the 30 member countries of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, the average is 56 percent. Minister Sibal has articulated an ambitious target of 30 percent of Indian students pursuing higher education by 2020.
Increasing access will require the expansion of enrollment at existing institutions and the creation of many new ones at all levels. The new world-class universities will only contribute a small fraction of the required increase in enrollments throughout India, but they will play an especially prominent role in India’s future development.
First, however, these universities must be built, and that is what I will speak about today: the challenge of building world-class universities.
A great research university is not built from the bricks and mortar of its campus, but of the students and scholars who inhabit it, and the discourse and ideas they share. A university exists not for the purpose of handing out diplomas to those who go through its doors, but to advance knowledge and to educate young people to become critical thinkers and society’s leaders. Building a world-class university is far more than a construction project – it is building a community of knowledge, far more than it is building a campus. A world-class university avails its students not just of courses of study, but of an environment that facilitates learning and growth in all areas of human endeavor. The university is composed of many things: a distinguished and engaged faculty; broad library and museum collections; state-of-the-art laboratories and computing resources; and a wide range of extracurricular, cultural and athletic activities, to name just a few essential components.
At the most fundamental level, a world-class university contributes to the world in three ways: through research, through education, and through institutional citizenship.
First, by facilitating advancements in science, technology, and medicine, research universities help spur economic prosperity and the advancement in the health and quality of life in communities across the world.
Second, by educating students, great universities prepare the next generation of leaders, leaders who will be able to tackle new problems and new situations with maturity and flexibility and who see the world with curiosity and an open mind.
Third, by acting as models of institutional citizenship, world-class universities contribute to the betterment of society and instill in their students social responsibility and an appreciation of service to their communities.
Let me discuss each role of the university in turn.
Inspiring innovation
First and foremost, a world-class university must have a world-class faculty. This serves as the backbone of any institution. For a broad, comprehensive university to be considered world-class it must have a faculty that, through its research, is making significant contributions to the advancement of knowledge.
In our "knowledge economy," nations prosper by virtue of their capacity to innovate – to develop and introduce new products, processes, services, and even, new ways of thinking. The extent to which such innovation happens is a function of the continuing advance of science.
As the principal source of basic research, comprehensive universities playa fundamental and irreplaceable role in encouraging economic development and national competitiveness. This basic research is motivated by the quest for intellectual discovery, not some practical objective-but in the long run, it is the wellspring for all commercially oriented research and development. That fact, that fundamental research occurs within the university – rather than in government laboratories, non-teaching research institutes, or private industry – is an essential element of allowing a university to realize its full potential. When researchers are isolated in research institutes, students – especially undergraduates are deprived of exposure to first-rate scientists, their methods, and their research. Absent the best scientists, the quality of teaching will suffer, and the curriculum is less likely to include the most novel thinking and innovative approaches.
World-class research requires substantial resources, and it is important to allocate these resources to produce maximum social benefit. This is one area where America has far outstripped the rest of the world, by allocating its public funding for research not by seniority and not by political give-and-take, but through the strict meritocracy of peer review. India would be well advised to adopt this model.
The research undertaken in universities must not stay in the academic buildings and laboratories where it is born. To drive national innovation, it must move from theory to practice, and the university plays a key role in this process as well. Engagement with industry is a central function of the modem research university, as commercializing faculty inventions benefits both the university and the broader
society.
Training future leaders
Second, just as faculty members contribute, through their scholarship and research, to the intellectual vigor of their nation and the world, they also serve to shape the future leaders of their nation and, again, the world.
The phrase "the knowledge economy" that is so often spoken about would seem to suggest that universities impart to young people what is most obvious – that is, knowledge. But the best universities do not practice the mere transfer of knowledge from teacher to student. They focus not on the mastery of content, but on the development of their students’ capacity for independent, critical thinking.
Universities exist to teach young people how to think, not what to think. The best American universities seek to educate undergraduates not to be experts in a particular field, but to be creative, flexible, and adaptive; to approach problems critically and to collaborate with others to solve them; and to be able to understand different cultures and adapt to new environments. Universities like Yale train undergraduates not for a profession, but for life.
The method of education employed by America’s most selective universities what we know as the "liberal education" of undergraduates – is particularly well suited to preparing students to enter the rapidly-changing modem world. Courses are not principally about a student mastering a body of knowledge, but about that student’s mind being stretched. This must be a guiding light in the creation of a course of study: as many classes as possible should be small, small enough to take shape as active discussions, not as lectures passively attended. Students must be challenged not to memorize, but to analyze. Professors must serve as mentors, as sources of inspiration, not merely as lecturers and graders.
Students, too, should not find their development limited to the classroom. Students at Yale often say that they learn more over meals with their peers in university dining halls than they do in classrooms and lecture halls. In addition, extracurricular activities- producing a play, singing in an a cappella group, writing for a campus publication – help teach skills in teamwork, communication, and collaboration that students later put to use as their careers develop.
Bettering society
Third, a world-class university leads by example, both in its local community and in the-world. Acts of institutional citizenship have benefits on two levels: they represent a positive force for human welfare, and they also inspire students to embrace social responsibility in their own lives. To illustrate this point, I will give examples of institutional citizenship both locally and globally.
When I became Yale’s president in 1993, the city of New Haven had a distinctly negative external image. As soon as I took office, we created a comprehensive strategy to engage with our surrounding community, partnering with public officials and neighborhood groups to better the city in which we live. Our initiatives included an internship program to allow students to work in schools, community service organizations, and local government; a Homebuyer Program to subsidize home purchases by our faculty and staff in neighborhoods around the campus; a concerted effort to spin-off Yale research into commercial ventures, particularly in biotechnology and medicine, and a major investment in the redevelopment of the downtown retail district. As a result of these actions, our community has been dramatically strengthened.
On a more global scale, consider the issue of reducing carbon emissions. The problem of global warming requires a multinational solution, and no solution will succeed without the cooperation of the United States and India. But universities can and should – play an important role in the effort to curtail global warming, both in their research and in setting standards for their own carbon emissions. In 2005, Yale made a commitment to reduce carbon emissions to 10 percent below our 1990 level by the year 2020, which equates to a 43 percent reduction in our 2005 carbon footprint. If the nations of the world were to negotiate such a reduction in carbon emissions later this year at their meeting in Copenhagen, the planet would be much better off.
Of course, we acknowledge that even the most ambitious sustainability efforts at the world’s universities will not have a measurable impact on global carbon emissions. But in keeping with our mission as a teaching institution, we seek to inspire our students and lead by example. And I believe that the collective leadership of the world’s universities on this important issue may very well serve, over time, to make meaningful global cooperation more likely.
Conclusion
There is no doubt that expanding access to higher education in India is an imperative, and Minister Sibal and others should be commended for understanding its importance. Expanding access to higher education will raise the general standard of living and create avenues of upward mobility for the most disadvantaged. With adequate investment of resources, expanding access is an achievable objective; it has been done before, in Europe and Japan following the second World War, and in China within the last eleven years.
But building world-class universities is a Herculean task. It has never been done before in one concerted effort, by one country. And it requires more than money. But if India succeeds, the impact on Indian society and its aspirations to world leadership will be limitless. It is through world-class universities that the seeds of innovation are planted arid the next generation of leaders acquires the capacity to lead. As this dream is pursued, it will be important to ensure that even these elite universities are accessible and affordable, and not merely available to those whose families can pay for it.
The challenge is immense, but the potential gains are commensurate with the challenge. Through their research, teaching, and institutional citizenship, a new set of great universities will strengthen this society, and the people of India – and of the rest of the world – will reap the benefits.
November 9th, 2009
Following is an excerpt from a report in Pioneer.
Chief Minister Naveen Patnaik has given green signal for the RVS Educational Trust to set up the proposed medical college and hospital in Balangir. Approving the recommendations of a high-level committee, he has asked the Western Odisha Development Council (WODC) to go ahead with an MoU for the purpose.
… Coimbatore-based RVS Group of Institutions, led by Dr KV Kuppusamy, is managing 87 educational institutions in the country. … The WODC had invited expression of interest for the medical college and hospital in Balangir last year in view of Shree Balaji Education and Charitable Trust backing out of the project.
The RVS Group would invest at least Rs 100 crore, while the WODC would provide a Rs 10-crore grant and 25 acres of land in Balangir. The medical college would have an intake capacity of 100 with a 300-bed hospital at its initial stage. Subsequently it would be enhanced to a 500-bed hospital and gradually to a 1,000-bed super speciality hospital, said sources in the WODC.
November 8th, 2009
Update:
HRD Minister Mr. Kapil Sibal spent last several days in the US trying to convince top US universities to collaborate and open branches in India. His talk at MIT is here http://techtv.mit.edu/tags/5218-sibal/videos/4310-mit-india-forum-2009. (Thanks to a commentator at Abi’s blog for the pointer.)
I wish some people of Orissa had not created road block for Vedanta University. If it had made progress as scheduled then it would have put the Bhubaneswar-Puri area in the map of top knowledge centers of India and there would have been a higher chance of some good foreign (especially US) universities thinking about having some operations in Orissa. As it stands now Orissa may lose the window of opportunity it has. Unless Orissa quickly positions itself among the top knowledge centers of India, the top foreign universities will give it a skip and it may again take a long long time for Orissa to catch up.
November 5th, 2009
Following is a letter that Dr. Karmee has sent to many people. This is an excellent work. It is well researched and based on something unique to the location, the Gandhamardan Hills of Baragarh and Balangir. (Considering that many in Orissa may not be aware of Gandhamardan Hills being in Orissa and/or its medicinal values, I have a companion piece on it at https://www.orissalinks.com/orissagrowth/archives/2776.)
I hope others will also focus on unique aspects and attributes of other parts of orissa and write to the higher education task force (HETF) about it.
Respected Mr. Patnaik, CM of Odisha and Members of the Higher Education Task force,
I appreciate the formation of higher education task force by the state government. Also, I am hopeful that such innovative steps will definitely sharpen the higher education of Odisha.
Sirs,
I would like to request the higher education task force to recommend the establishment of a “National Institute of Ayurveda” in Gandhamardan area in western Odisha. I am sure many of us are aware of the potential of Gandhamardan mountain and medicinal plants in it.
In this document, I am presenting the details about the “Gamdhamardan mountain as a reservoir of medicinal plants” with scientific references; thereby, making a case for the establishment of a National Institute of Ayurveda.
I am sure our respected CM, who is the author of the “Garden of Life: An introduction to the Healing Plants of India” will take this matter seriously. Also, I am hopeful that the higher education task force will take the necessary steps; so that, “the medicinal plants in Gamdhamardan mountain” will not get lost with time.
Please have a look on the following write-up for further details.
Thanking you with best regards,
Sanjib
1. “National Institute of Ayurveda” is a must in Gandhamardan area: Introduction and Analysis:
Gandhamardan mountain range is known world wide as a reservoir for medicinal plants. It is located in the western Odisha. More specifically, it is located in between Balangir and Bargarh district (Figure 1).
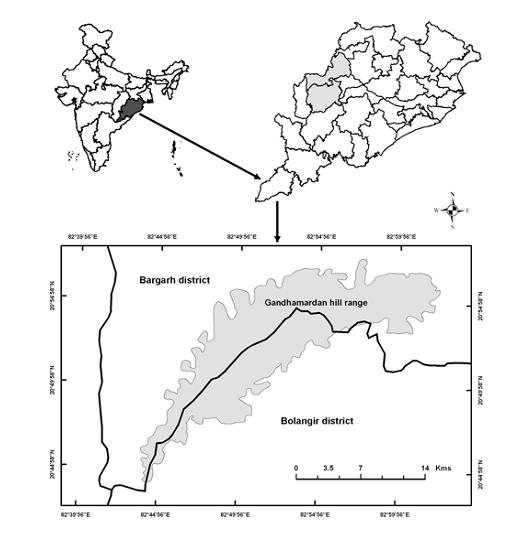
Figure 1 Map showing location of Gandgmardan mountain in between Balangir and Bargarh district
Many eminent scholars of life sciences have done a lot of research on the medicinal plants available in this mountain range. In fact, this hill range is legendary. It has found a place in folklore and mythology -of how Hanuman plucked Bisalyakarani, a medicinal plant, from this hill to save the life of Laxman in the battle of Lanka in “The Ramayana”. In addition, it is known to the whole world how this hill range was at the centre of one of the most prominent ecological movements, that is, the battle between environmentalists keen on protecting aryurvedic plants and the then state-owned Bharat Aluminium Corporation.
Apart from this, there are many scientific journals and books that are mentioning about the potential of medicinal plants available in Gandhamardan mountain (see the reference list)1-5. The state/central govt must establish a “National Institute of Ayurveda” in this place. Right now, both Balangir and Bargarh (Paikmal) each have one Ayurvedic College. Establishing a national level institute on Ayurvedic Medicine will help to a great extent to these colleges by carrying out research in emerging areas. Recently, research on ayurvedic medicine is attracting considerable attention in India and abroad.
It is important to note that, significant developments have boosted systematic research on different aspects of ayurveda and traditional medicine in India. They include the Golden Triangle project jointly managed by CSIR, ICMR and AYUSH; the New Millennium Indian Technology Leadership Initiative (NMITLI) of CSIR and various schemes of DST and DBT.
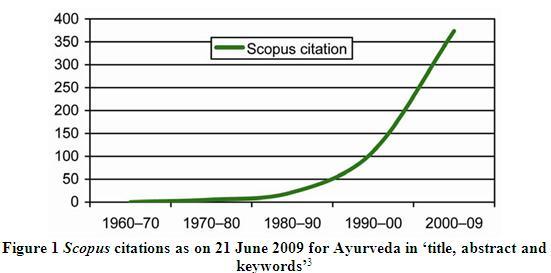
Additionally, ayurveda is also entering to the mainstream “Drug Discovery”. Following graph show the growing demand of research on Ayurvedic medicine.
In addition to this, a paper by “Reddy and Pattnaik” from the Forestry and Ecology Division, National Remote Sensing Centre, Hyderabad 500 037, Andhra Pradesh, India points out many interesting facts about “Gandhamardan hill” 4.
It states that, after analyzing and studying the plant resources of Gandhamardan hill range a total of 912 vascular species belonging to 556 genera under 142 families were found. Herbs dominate the flora followed by trees, climbers and shrubs.
Therefore, proper conservation and management plans are needed to save the natural resources, especially medicinal plants, of this sacred hill range. Many botanists fear that this reserve of medicinal plants could be lost in the next few years if proper care is not taken and the indiscriminate collection and smuggling of herbs by local villagers is not stopped. The state forest department which is supposed to guard this botanical wealth is not able to do enough to stop all these developments because they lack of the knowledge and expertise about these plants. In fact, they have no clue which are useful medicinal plants and which are not.
In addition, in these places there is no organized way of farming of the medicinal plants. They just grow in the wild. Therefore, it is very difficult to guard these species. Taking the advantage of this situation any villages or smugglers can walk into the forest and collect the herbs. It is very important that the government should takes steps to grow these plants, harvest these properly, and finally do the marketing of these medicinal plants and herbs in a well organized manner. It should take care of the cultivation and preservation of these plants like it is doing for other forest products like sal seeds or kendu leaves etc.
However, intellectually this problem can be solved by establishment of a National Institute of Ayurveda. The above discussion/ description/ scientific observation strongly suggests the establishment of a National Institute of Ayurveda near Gandhamardan mountain.
2. Following are some of my points in support of establishing a National Institute of Ayurveda in Gandhamardan area:
* West is very much keen on establishing institute on ayurveda. One such successful institution is the National Institute of Ayurvedic Medicine established by Dr. Scott Gerson, USA, (http://niam.com/corp-web/index.htm). This is an example of an institute that has carried out research into Ayurvedic practices to a great extent. In this context, we must use our native expertise. In addition, the National Institute of Ayurvedic Medicine, USA can be a collaborative partner for establishing an institute Gandhamardan area.
* This mountain is very important to all of us and to the world. We should use our natural medicinal resources very judiciously. It is also very surprising that no steps have been taken for the preservation of these high-valued plants. It is the right time to establish a National Institute of Ayurveda in this area.
* As we know this mountain range is a reserve for medicinal plants. Therefore, it will provide adequate environment for cutting edge research/studies in different areas of ayurvedic medicine per international standard.
* Establishment of a National Institute of Ayurveda will help for organized way of farming the medicinal plants; which just grow in the wild. This will also help in preserving different rare species of plants.
* This Institute will provide a boost to the ongoing research/academic activities by Ayurvedic College Balangir and Shri Nrusinghanath Ayurved College Paikmal, Bargarh on this area. Along this line, establishing a National Institute of Ayurveda will make this place a leader in this area of science in national/international level.
* This step will attract companies like Dabur, Ayur, and others to set-up labs/companies in this area.
* From the above discussion it is very clear that research fundings are already available from the leading agencies of India like CSIR (Council for Scientific and Industrial Research), DST (Department of Science & Technology), and DBT (Department of Biotechnology). So, there will be no problem in setting up labs and developing infrastructure.
* There is a lot of synergistic research going on between Ayurvedic, Homeopathic and Allopathic branches of medicine. This is very clear from our day-to-day life as Allopathic doctors often prescribe medicines of Dabur, Neem, etc. Therefore, establishment of such an institute will further enhance the research between this National Institute of Ayurveda with other institutes viz. VSS Medical College, SCB Medical College etc. of the state.
3. The following steps need to be taken to establish a National Institute of Ayurveda in Gandhamardan
* It is important to look in to the web-site of these model Institutes viz. National Institute of Ayurvedic Medicine, USA (http://niam.com/corp-web/index.htm); Gujarat Ayurved University Jamnagar, Gujrat, India (www.ayurveduniversity.com); Rajasthan Ayurved University, Jodhpur Rajasthan (http://www.raujodhpur.org/aboutus.html); National Institute of Ayurved, Jaipur, Rajasthan (http://nia.nic.in/); Ayurvedic university, Hoshiarpur, Punjab; (http://www.financialexpress.com/news/punjab-clears-first-ayurvedic-university-in-hoshiarpur/517911/; This seems to be a new Institute).
* Immediately, the state govt. should present a proposal to the HRD Ministry for establishing National Institute of Ayurveda in Gandhmardan area.
* Along the line of the above institutes, the state govt. in collaboration with govt. of India must establish a National Institute of Ayurveda in Gandhamardan area.
References:
1. Netra Bhanu Pradhan, Gandhamardan – A treasure House of Medical Plants, Navaratna Journal, Jan-Feb, 2008, 41-44.
2. Ayurveda: scientific research and publications, Current Science, 2009, 97( 8), 1117-1122
3. C. Sudhakar Reddy and Chiranjibi Pattanaik, An Assessment of Floristic Diversity of Gandhamardan Hill range, Orissa, India. Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 16(1): 29-36, 2009
4. Following are some of the research papers taken from the reference list of the paper 3 (Papers only with the name Gandhamardan are taken)
Brahmam, M. and Saxena, H.O. 1990. Ethnobotany of Gandhamardan hills – Some noteworthy folk medicinal uses. Ethnobotany 2: 71-79.
Brahmam, M. and Saxena, H.O.1990. Phyto-chemical screening of the plants of Gandhamardan hills of Orissa (India) for tannins, saponins, flavonoids and alkaloids. Asian J. Plant Sci. 1: 71-79.
Misra, R.C. 2004. Therapeutic uses of some seeds among the tribals of Gandhamardan hill range, Orissa.Indian J. Traditional Knowledge 3: 105-115.
Misra, R.C. and Behera, G. 1998. Ecological status of Gandhamardan forests using remote sensing techniques. In: Biodiversity Conservation: Problems and Prospects. Proc. National Seminar on Biodiversity Conservation, Bhubaneswar, India, pp. 75-80.
Misra, R.C. and Das, P. 1998. Vegetation status of Nrusinghanath – Harishankar complex, Orissa. J. Econ.Taxon. Bot. 22: 547-554.
Mishra, R.C. and Das, P. 2003. Wild poisonous seeds: Some notable species from Gandhamardan Hill ranges of Orissa. J. Econ. Bot. 27: 513-518.
Misra, R.C. and Das, P. 2004. Vegetation stratification of Gandhamardan hill range, Orissa using remote sensing techniques. J. Econ. Taxon. Bot. 28: 429-438.
Mishra, R.C., Panda, P.C. and Das, P. 1994. Lesser known medicinal uses of plants among the tribals of Gandhamardan hill ranges, Orissa. In: Gupta, B.K. (ed.), Higher Plants of Indian Subcontinent, Vol. III, Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh Publications, Dehra Dun, India, pp. 135-142.
Mishra, R.C., Panda, P.C. and Das, P. 2001. A taxonomic study of the ferns and fern allies of Gandhamardan hills, Orissa. J. Econ. Taxon. Bot. 25: 577-590.
Panigrahi, G. 1963. Gandhamardan Parbat, Orissa – A potential source of important indigenous drugs. Bull. Reg. Res. Lab. 1: 111-116.
Pattanaik, C. and Reddy, C.S. 2007. Medicinal plant resources of Gandhamardan hill range, Orissa: An urgent need for conservation. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 30: 35-38.
Raju, D.C.S. 1960. Vegetation pattern of Gandhamardan hills. Bull. Int. Soc. Trop. Ecol. 1: 21-22.
Saxena, H.O. and Brahmam, M. 1995. Vascular flora of Gandhamardan hills. J. Econ. Taxon. Bot. 19: 113-132.
5. NOTE: This is not the complete list of references. Because of time limitation I have collected as much as I can.
November 4th, 2009
Following in an excerpt from a report in Times of India.
An unemployed MSc or Phd basic science student can write a proposal to the department of science and technology on any project that would have useful results — either in terms of a product or in terms of enhanced knowledge, or new formulations in basic sciences. The proposal is evaluated by experts, and if okayed, the student gets the grant for
two years.
‘‘Students may not want to do an MSc or Phd in basic sciences, fearing they won’t land jobs. This hits research in basic sciences as well as the student ratio and strength. If there is some sort of security and an assured financial support period, students would feel confident to take up MSc or Phd in basic sciences. That way, research benefits,’’ said an official of the department of science and technology.
The ministry is planning an awareness drive across the country on the science allowance.
… ‘‘The money coming from the DST is good and will be enough to help the student coast through a year or two. We expect a student to come up with a project that would be job-enabling, as experience on the project would count in job offers. The good thing is that students would not be penniless for the two-year period. The science ministry takes care of the student until he or she finds a job,’’ the official said.
November 3rd, 2009
Following is from http://www.barandbench.com/index.php?page=brief&id=248&full=.
The National Law University, Orissa (NLUO) was formally inaugurated by the Chief Justice of India, K.G. Balakrishnan. Chief Minister Naveen Patnaik, the Chief Justice of the Orissa High Court, I. M. Quddusi, State Higher Education Minister Debi Prasad Mishra and Minister of Law Bikram Keshari Arukha were present at the ceremony.
Bar & Bench talks to the dynamic Vice Chancellor of National Law University, Orissa, Dr. Faizan Mustafa, on his vision for NLUO and why NLUO is different from the other national law universities (NLUs).
Move from Interdisciplinary approach to integration of knowledge
NLUO is the first University in the country to integrate the B.A., LLB (Hons.) program with the BBA, LLB (Hons.) program. Students can opt for courses from both disciplines of study, and thus, can combine humanities courses with a human resources and marketing course. NLUO has also introduced innovative new courses in legal journalism and mass communication, in conjunction with the law degree.
Students from over 22 states and excellent infrastructure
In the first year, students from 22 states have joined NLUO. Our admission test has been rated as one of the best and some people have said it is tougher than the Common Law Admission Test (CLAT). We hope to receive a better response next year when people see our infrastructure and campus. Currently people think Cuttack is far away from the "Metros" and won’t have good faculty and infrastructure facilities. We have spent more than Rs. 1 crore ($208,000) on the books alone. Our hostel facilities for students are amongst the best. The legal education space in the eastern part of India was in shambles. We hope to make a difference here.
Best of both worlds- Senior Faculty, alumni from NLUs and faculty from foreign law schools
During our times, teachers were good while students were bad, since law was the last option for many students. But with the advent of the national law schools, the quality of students has become excellent. I need thank my Senior from college, Dr. Madhav Menon, for his efforts in bringing change into the legal education space. Self-financing Law Universities like us cannot continue to run without quality faculty. There is an unwritten rule in our Universities where we encourage alumni from other NLUs and people who have taught abroad to come and teach in NLUO. We already have faculty who have had experience in other western countries, along with Senior Faculty from other NLUs. For example, the former Vice Chancellor of NLSIU, Bangalore, Dr. N.L. Mitra is one of the faculty members, as is Senior Professor Ajjappa, who has taught at various Law Universities. We want to bring the best of both worlds together, so students can benefit from such vast experience.
Also, I think Law Faculty should not be judged on UGC or other pay scales in self-financing institutions like ours. We need to provide other incentives to faculty to lure them away from private corporations or high paying jobs. If we have to be a third generation Law University, we need to provide the best for the Faculty and students.
NLUs are producing ‘Soft’ Lawyers
The CJI in his welcome speech said, "The NLUs have failed in so far as producing lawyers for the Bar." Constant criticism against the NLUs is that they are producing ‘Soft’ lawyers who opt for Air Conditioned office spaces instead of joining ‘real ligation’ and or opting for judicial services. If we want to increase the quality of our Judges, we also need to increase the quality of the lawyers. One space where NLUO intends to bridge this divide is to concentrate on "traditional lawyering" and not merely corporate law.
New Areas of Legal Practice
NLUO will focus on mining law, water law, food law, energy law and agriculture law. Our country continues to be driven by agriculture and yet, very little importance is attached to agriculture and the legal issues around it. While Corporate Law and IP Law are important for the economy, equal importance has to be given to other areas of practice. Orissa is losing Rs. 20,000 crores ($4.16 billion) every year due to the center-state divide on resources. We plan to have centers on these areas to conduct exhaustive research and recommendations.
I want to build a socially relevant Law University. I encourage people to come, see the University and provide us with comments on improving it.
November 3rd, 2009
Update: Tathya has an article and pictures on the current status of the construction of AIIMS Bhubaneswar. One of the pictures is given below. Tathya.in says: "Kolkota based Unit Construction has taken up the construction job, while the PSU, Hospital Services Consultation Corporation (HSCC) is the civil consultant for this projects."

More details on the tender is at http://mohfw.nic.in/Index6aiims.htm:
The above tender is about the hospital and medical college. Earlier in May 2008, tenders were floated for the housing complex. See https://www.orissalinks.com/archives/1121. (Even older links related to tenders for the AIIMS-like institution in Bhubaneswar are at https://www.orissalinks.com/?p=970.) In June 2009 it was reported that:
- Out of the 14 blocks of the AIIMS, the roof works of eight blocks have already been completed.
- An alternative road has already been constructed for the Sijua village and 90 per cent work has already been completed.
- Steps have been taken to remove the high-voltage transmission line.
I hope additional progress has been made with respect to the housing construction.
November 2nd, 2009
IISc Bangalore faculty Prof. Abi has a nice article on this in the IIT Kharagpur student magazine Scholar’s avenue. Following are some excerpts arranged as bullet points.
- Salary: Going by the present, post-SPC salaries, you’ll start as an assistant professor at Rs. 6 lakhs, at the end of your career, you’ll be at over 12 lakhs.
- ‘benefits’: allowances (house rent, transport, telephone and internet), social security contributions (pension or provident funds, career-end bonus, etc) and perks (medical insurance, leave travel concession, for example). The value of these benefits could easily exceed 50 percent of the salary.
- consulting: It can give you the satisfaction of solving some real world problems. It can be a great source of ideas for long term research. Most importantly, it also has the highly desirable property of giving you some extra cash!
- IIX salary is not only fully protected, it’ll also (a) keep up with inflation, (b) keep rising (through annual increments) and (c) see substantial jumps every decade or so. To sweeten things even more, IITs are planning to introduce incentives to reward extraordinary performance (and I’m sure other IIXs will follow suit).
- As an IIX faculty member, you’ll enjoy a couple of features that are not available to engineers and managers in industry (in both public and public sectors): two (or even three) months off every summer and a one-year sabbatical leave every seven years.
- As an IIX faculty member — and this may come as a surprise to you — you’ll also enjoy certain advantages over faculty in US universities.
- First, you don’t have to pay your graduate students, the government pays them.
- More importantly, the same research idea has a far higher probability of getting funded in India than in the US. This means that you’ll spend more of your time on actually doing research, than on writing grant applications seeking that ever-elusive funding.
- Finally, the autonomy, the choice and the flexibility: As an IIX faculty member, you’ll probably spend 30 to 40 percent of your time in teaching and related activities. The remaining time is yours, and yours alone — nobody tells you how to spend it. You could use it for research (for getting peer recognition), teaching (for your students’ adulation), and consulting (for money, and collaboration with industrial partners). There are other academic pursuits as well: writing books and popular science articles, teaching kids in local schools and colleges, learning about new and emerging fields, etc.
November 2nd, 2009
Following is from PIB release http://pib.nic.in/release/release.asp?relid=53747.
|
Update on AIIMS-like institutions tenders/nits worth Rs. 1908 Cr for the main civil packages for six new AIIMS-like institutions invited
|
| |
17:38 IST |
Government of India has launched the Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY) with the objective of correcting regional imbalances in the availability of affordable/reliable tertiary healthcare services and also to augment facilities for quality medical education and research in the country. Under the Ist phase of this scheme, six new AIIMS-like institutions are being set up, one each in the States of Bihar (Patna), Chattisgarh (Raipur), Madhya Pradesh (Bhopal), Orissa (Bhubaneshwar), Rajasthan (Jodhpur) and Uttarakhand (Rishikesh) at an estimated cost of approximately Rs 820 Crores per institution. Each of these institution will have a 960 bedded hospital (500 beds for the medical college hospital; 300 beds for Specialty/Super Speciality departments; 100 beds for ICU/Accident and trauma. In addition 30 beds for Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation (PMR) and 30 beds for Ayush have been kept. This would be full fledged multi-disiciplinary healthcare institution offering facilities in 42 speciality/super-speciality disciplines. Medical College will have an annual intake of 100 UG intake besides imparting PG/doctoral courses in various disciplines. Nursing College will also have 100 UG intake and 25 PG intake annually.
The respective State Governments have provided 100 acre land free of cost. The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt. of India engaged eminent architectural firms to prepare the designs and drawings. The architectural/DPR Consultants were selected on global competitive basis. The Project Consultants have also been selected for each site on the basis of open competitive bids. Project Cell at the sites comprising engineering, finance and administrative set up has been constituted and posts are being filled up on deputation basis from other Central Govt./State Govt. organizations.
The construction work has been split into 7 different packages, depending on the functional /sequential requirement and core specialization needs. Tenders/NITs for the main civil packages viz. (i) Civil works for Medical College, Nursing College, AYUSH and Hostels, (Patna, Raipur, Bhopal); and (ii) Civil works for Hospitals – OPD Complex including all internal services and specialized works are being invited. The total cost of these two packages is between Rs.250 – 300 Crore for each site, totaling Rs. 1908 Cr. for all six sites.
The salient features of the tenders /NITs issued on 2nd Nov. are as follows:-
(i) All detailed engineering drawings have been prepared.
(ii) Environmental clearance has been obtained for 5 out of 6 sites and is being obtained for the remaining site (Bhopal).
(iii) Medical College Complex will be built in 15 months time.
(iv) The Hospital – OPD complex is to be built in 24 months.
(iv) Apart from ensuring timely payment, there are very strong incentive clause for early completion with a bonus of 1% of the tendered value per month computed on per day basis, subject to maximum of 5%.
(v) Like-wise there is a strong disincentive clause/penalty if the project is delayed.
Pre-bid Conference is scheduled for 16th November, 2009. Last date of receipt of bids would be 3 Dec 2009
************
October 30th, 2009

October 30th, 2009
Following is an excerpt from a report in expressbuzz.com.
The Centre has sanctioned funds for establishment of Government polytechnics in 14 districts of the State.
Each of the institutes will receive a one time grant of Rs 12.30 crore from the Centre for infrastructure development while the State Government will take care of the recurring expenditure, including staff salary and administrative expenses.
The Government polytechnics will be located in districts having no such institutes.
Orissa has 13 technical institutes including three women polytechnics offering diploma courses in various trades. However, these institutes are limited to only nine districts and most of them are located in coastal region.
The new polytechnics will be opened in seven Naxal-affected districts of Malkangiri, Nabarangpur, Gajapati, Sambalpur, Jajpur, Nayagarh and Deogarh.
The other districts selected for the Centrally assisted technical institutes are Boudh, Nuapada, Kalahandi, Kendrapara, Jagatsinghpur, Puri and Sonepur.
Sites for the proposed polytechnics have been selected in respective district headquarters.
The Government will provide at least 10 acres of land for each of the polytechnics free of cost.
The new polytechnics will start functioning from the next academic session. …
According to a conservative estimate, each polytechnic will have at least 50 staff. The Government will take a decision on recruitment of staff on permanent or contractual basis.
The Government had already submitted a proposal to the Centre for financial assistance for opening Government polytechnics in the remaining seven districts.
October 29th, 2009
The following list of state agricultural universities is compiled from the information in http://www.icar.org.in/?q=universities.htm. This list is also available at the pages of Indian Agricultural Universities association.
Andhra Pradesh
- Acharya NG Ranga Agricultural University, Hyderabad
- Sri Venkateswara Veterinary University, Tirupati
Assam
- Assam Agricultural University, Jorhat
Bihar
- Rajendra Agricultural University, Pusa, Samastipur
Chhatisgarh
- Indira Gandhi Krishi Vishwavidyalaya, Raipur
Gujarat
- Anand Agricultural University, Anand
- Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagarh
- Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari
- Sardarkrushinagar-Dantiwada Agricultural University, Bansakantha
Haryana
- Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar
Himachal
- CSK Himachal Pradesh Krishi Vishvavidyalaya, Palampur
- Dr Yashwant Singh Parmar Univ of Horticulture & Forestry, Solan
J & K
- Sher-E-Kashmir Univ of Agricultural Sciences & Technology, Jammu
- Sher-E-Kashmir Univ of Agricultural Sciences & Technology of Kashmir, Srinagar
Jharkhand
- Birsa Agricultural University, Ranchi
Karnataka
- University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore
- University of Agricultural Sciences, Dharwad
- Karnataka Veterinary, Animal and Fisheries Sciences University, Bidar
Kerala
- Kerala Agricultural University, Trichur
Madhya Pradesh
- Jawaharlal Nehru Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Jabalpur
Maharashtra
- Dr Balasaheb Sawant Konkan Krishi Vidyapeeth, Ratnagiri
- Dr Panjabrao Deshmukh Krishi Vidyapeeth, Akola
- Maharashtra Animal Science & Fishery University, Nagpur
- Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth, Rahuri
- Marathwada Agricultural University, Parbhani
Orissa
- Orissa Univ. of Agriculture & Technology, Bhubaneswar
Punjab
- Guru Angad Dev Veterinary and Animal Science University, Ludhiana
- Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana
Rajasthan
- Maharana Pratap Univ. of Agriculture & Technology, Udaipur
- Rajasthan Agricultural University, Bikaner
Tamil Nadu
- Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore
- Tamil Nadu Veterinary & Animal Science University, Chennai
UP
- Chandra Shekar Azad University of Agriculture & Technology, Kanpur
- Narendra Deva University of Agriculture & Technology, Faizabad
- Sardar Ballabh Bhai Patel Univ. of Agriculture & Technology, Meerut
- UP Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhaya Pashu Chikitsa Vigyan Vishwa Vidhyalaya evam Go Anusandhan Sansthan, Mathura
Uttaranchal
- Govind Ballabh Pant University of Agriculture & Technology, Pantnagar
West Bengal
- Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Kalyani
- Uttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Cooch Bihar
- West Bengal University of Animal & Fishery Sciences, Kolkata
Manipur
- Central Agricultural University, Imphal
The Indian Agricultural Universities association also includes the following deemed universities,
and the following university that has programs in Agriculture
October 26th, 2009
Regardless of the attempt to industrialize Orissa, for a long time to come a large number (perhaps majority) of people in Orissa will still use agriculture for their livelihood. Also various reports mention that Agriculture is the top focus of the current government in Orissa. With that in mind, I am thinking to push for a second Agricultural University in Orissa. Many other states already have more than one agricultural university. (See the lists here, here, the ICAR list and the wikipedia entry.) I would like feedback on what would be a good location for the second Agricultural University in Orissa.
My initial instinct says Bhawanipatna/Kesinga, as I have heard about Kalahandi’s agricultural potential; also that location creates a good geographical balance. That was probably one of the main reasons the government earlier announced an agricultural college in Bhawanipatna. If I could get some more supporting data and arguments I would like to push that the proposed agricultural college in Bhawanipatna be made into a university and become the second Agricultural University in Orissa.
October 26th, 2009
Next Posts
Previous Posts






