The website of this summit is http://www.ficci.com/past-Events-page.asp?evid=20665. Following are excerpts from the press release on Dr. Montek Ahluwalia’s speech.
Inaugurating FICCI Higher Education Summit 2011: Strategies for Expansion in Higher Education in India’, Mr. Ahluwalia said, “The challenge before planners, policy makers and educationists, both in the public and private sector, was of producing world class Indian universities that could be counted in the top 200 rating list.” In the next 20 years we must see a significant number of educational institutions in that category, he declared.
Mr. Ahulwalia also underlined the need to lend an international flavour to Indian universities by inducting international faculty. This would not happen unless the government removes the restriction on employment of international faculty, he said.
For higher education, the 12th Plan objective was expansion, equality of access and excellence. The aim was to raise the gross enrolment ration from the current level of 15 per cent to 30 per cent over the next 15 years. “Expansion of higher education has to be balanced with equality of access, especially for those living in areas where educational institutes did not exist,” he said.
Following are excerpts from the press release on Sam Pitroda’s speech.
Addressing the FICCI Higher Education Summit 2011, Mr. Pitroda said, “Higher education reforms are essential if the nation is to meet the serious challenge of skill shortage that will not allow the economy to grow at 8-10 per cent annually. While many of the recommendations of the National Knowledge Commission are in the process of being implemented, we are waiting for the government to act on the recommendations retailing to reform of higher education.”
“The debate on what needs to be done ought to be over, the time now is to focus on action,” he said and added that “the Bills have already been drafted but none of them have been tabled in or passed by Parliament.”
Mr. Pitroda’s concern found an echo in FICCI President, Mr. Harsh Mariwala’s suggestion that although education continues to be a priority sector during the Twelfth Plan, unless the reform agenda initiated by the Ministry of Human Resource Development in the 11th Plan is carried forward within a stringent timeframe, the demographic dividend of a young population could become a demographic disaster for India as well as the world.
Mr. Mariwala hoped that the Foreign Education Providers’ Bill; Unfair Practices Bill; Tribunal Bill and the Accreditation Bill will be passed in the coming winter session of the Parliament and the National Commission for Higher Education and Research (NCHER) Bill 2010 and Innovation University Bill will be introduced in the winter session of the Parliament. The delay in implementation of the reforms is a serious impediment for the economic development of the country, he said and added that FICCI earnestly urges the political leadership to take cognizance of this fact.
Mr. Pitroda said that the government was creating a US$ 5 billion National Knowledge Network (NKN) which is expected to be ready in about nine months. The network would be a state-of-the-art multi- gigabit pan-India network for providing a unified high speed network backbone for all knowledge related institutions in the country. It would facilitate the building of quality institutions with requisite research facilities and creating a pool of highly trained professionals. The NKN will enable scientists, researchers and students from different backgrounds and diverse geographies to work closely for advancing human development in critical and emerging areas.
Following are excerpts from a report in Chronicle of Higher Education.
Mr. Sibal has said that private participation in higher education must be encouraged, and conference attendees agreed that if the government hopes to reach its goal of sending 30 percent of young people to college, both private and public participation are needed. The challenge, as always, is in weeding out the low-quality operators.
"The public perception of private higher education is in a range," said Montek Singh Ahluwalia, head of India’s Planning Commission, a top government policy-making body. "Many are good, but there is a problem of those not-very-good ones."
Mr. Ahluwalia argued that supply and demand will eventually eliminate the bad actors, but others disagreed.
"It will be difficult to weed them out," said M. Anandakrishnan, head of the Indian Institute of Technology’s Kanpur branch. Because there is more demand than supply, he said, it will take time for stakeholders to make discerning choices.
Another delegate, Sachi Hatakenaka, a British-based education researcher, argued that "private sector growth is good for quantity but not for quality."
… Still, said Mr. Agarwal, the next round of government higher-education planning will focus more on expanding capacity at existing institutions rather than adding new universities.
Some private players were hopeful that the government will look to the private sector more as an ally than an adversary in coming years.
November 16th, 2011
Following is an excerpt from a report in Economic Times.
"We will be spending close to $100 billion on education in the 12th plan period. This will be in addition to around $20 billion investment on IT," Pitroda said at the ninth Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) here.
He said the government was taking measures to open up the education sector for more private and overseas investments.
"We have to liberalise the education system. What we did to the economy in 1991 needs to be done to the education now," said Pitorda, who is also the head of National Innovation Council .
He said the government had shown commitment to revolutionise the education system but the pace of development was not satisfactory.
"We have made recommendations. Minister has to act. So far, they have not acted to my satisfaction," Pitroda said, referring to the recommendations of the National Knowledge Commission .
January 9th, 2011
The list is given below. As per a Times of India report NIT Goa has commenced operation.
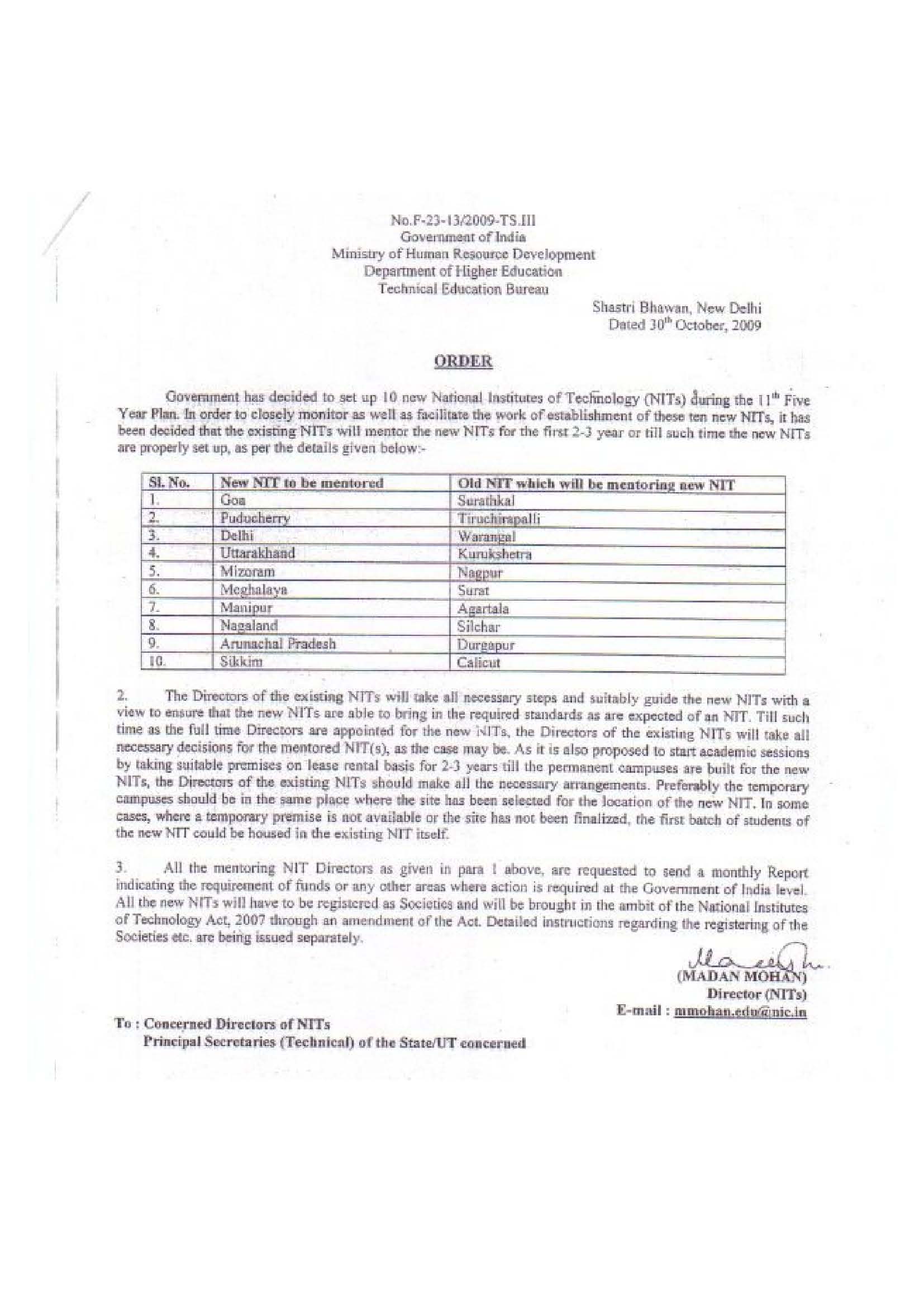
Related Links:
August 1st, 2010
Following is an excerpt from a report in Indian Express.
… Sibal had written to the PM seeking his intervention on three stuck schemes including the proposal to set up 20 new IIITs (Indian Institutes of Information Technology) on PPP basis, which was shot down by the Finance Ministry earlier this month. Of the other two stuck projects, one is meant to finance state universities and colleges, and the second is a Rs 2,000-crore scheme to set up 2,500 vocational schools across the country.
The PMO has now asked the Planning Commission to re-examine the projects.
Sibal is learnt to have brought to the PM’s notice how these projects were key to increasing the Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in higher education. India is looking at a GER target of 20 per cent by 2020 against a dismal 12 per cent at present.
… the ministry’s proposal — shared with all state governments last year — to incentivise states for setting up new universities and colleges has also hit a roadblock. The proposal is to provide Central assistance to state governments to the tune of 1/3rd of the capital cost for setting up of new universities and colleges and also for expansion of existing institutes. The state governments will be required to bear 2/3rd of the capital cost and recurring expenditure. In fact, states have already been asked to identify land and suitable locations for these new institutions and also prepare detailed project reports.
July 21st, 2010
For additional background and the list of 123 EBBs in Odisha see https://www.orissalinks.com/archives/1689. Following is from the PIB http://pib.nic.in/release/release.asp?relid=60782.
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs today approved the setting up of 1000 additional model schools as a benchmark of excellence in Educationally Backward Blocks (EBBs) through State Governments, thereby taking the total number of model schools to be set up through the State Governments to 3500.
The financial requirement for setting up 2500 schools under State Governments, which were approved by CCEA in November 2008, was estimated as Rs.9322 crore during the 11th Five Year Plan, of which the central share is Rs.7457 crore. Requirement for additional 1000 schools (current proposal) has been estimated to be Rs.3304 crore with the Central share of Rs.2478 crore. Thus the estimated Central share for establishing 3500 schools in the Government sector is Rs.9935 crore during the 11th Five Year Plan.
Each school will have 560 students, the total beneficiary for 3500 schools therefore being 19.60 lakh students. The programme will be implemented through the societies set up by the State Governments for this purpose.
The present proposal is meant for 3500 EBBs in 27 States/UTs, although the model school scheme will cover 6000 blocks in all States/UTs.
The salient features of the Scheme are as follows:
(i) Every EBB will be eligible for one model school under State Governments.
(ii) These schools to have classes from VI to XII or from IX to XII.
(iii) These schools to have norms and standards equal to or better than Kendriya Vidyalayas
(iv) Medium of instruction and affiliating board will be decided by the State Governments.
(v) 75% of the recurring and non-recurring cost, subject to scheme norms, will be borne by the Central Government except for special category states, for which the sharing pattern is 90:10.
The major impact of the scheme will be to open up access to quality secondary education to talented rural students. The scheme is expected to provide a major fillip to availability of good quality schools in rural areas, thereby nurturing talent in such areas. These schools are expected to act as pace-setting institutions and to have a demonstration effect on neighbouring schools.
April 24th, 2010
Following is an excerpt from a report in Business Standard by Bishnu Das.
The state government, in its proposal, has proposed to convert the existing Institute of Entrepreneurship Development (IED) at Bhubaneswar, a nodal agency of the Orissa government, to a national level institute for MSMEs. The proposed national institute for MSME would be in line with National Institute of Enterprise and Business Development, Noida, National Institute of MSME, at Hyderabad and Indian Institute of Entrepreneurship located at Guwahati. Since the Union government plans to set up three such new centres in the country, the state government intends to cash in on the opportunity. The state government has offered to provide the infrastructure including land belonging to IED for setting up this institute.
April 20th, 2010
Following is an excerpt from a report in Times of India.
The MSC Ed, an integrated six-year course (12 semesters), introduced in 2008 is the right way to master teaching skills. Offering quality teacher education programmes is the Regional Institute of Education that include innovative pre-service and in-service teacher training programmes and relevant research, development and extension activities.
The institute started as Regional College of Education in 1963, changed the name in 1994. It is one of the five such institutions established by the National Council of Education Research and Training (NCERT), New Delhi. The other institutes are located at Ajmer, Bhopal, Bhubaneswar and Shilong.
Prior to the six-year course, there was a two-year MSC Ed course for those who had completed BSC Ed, said Regional Institute of Education Principal GT Bhandage. "It had a good response and the students from all over the country would appear for the entrance exam. This course was conceived essentially to meet the demand of the higher secondary level in specific subjects like physics, chemistry and mathematics. Students who have passed out from this course were absorbed by Navodaya and Kendriya Vidyalaya," added Bhandage.
In 2008, MSC Ed course was introduced after completion of II PUC or equivalent. The idea was to catch them young and train them with pedagogic skills and develop adequate content competency crucial to a teacher education programme, said Bhandage.
The six years integrated course is a combination of BSc and MSC. The first four years, students study physics, chemistry and mathematics while in fifth and final year they can choose a specialization subject.
After completion of the course one can get into Higher Secondary Schools or can do research.
… The admissions are made on all India basis through an entrance exam. The selection will be based on the performance in the qualifying exam and entrance exam.
For details log on to www.riemysore.ac.in or call 514515/ 2514095.
RIE Mysore has a website at www.riemysore.ac.in. I have not been able to find a web site for RIE Bhubaneswar. I wonder if RIE Bhubaneswar offers such a course.
Considering the implementation of RTE, there is a big need for more and better trained teachers and educational administrators (headmasters, principals, vice-principals, etc.). To achieve that the government of India should upgrade the RIEs to National Institutes of Education and make them Institutions of National Importance. This will attract the attention of more good students towards a teaching and teaching administration career. The government should incraese the number of seats and number of programs in these institutes and intrdoce programs for creating top-notch Educational administrators.
April 14th, 2010
Following is an excerpt from a report in Telegraph:
The association’s board of governors has recommended the feasibility of 78 more Kendriya Vidyalayas (KV) as part of the process initiated by the HRD ministry for expanding the network of such central schools during the 11th plan period. The feasibility report included two KVs in Cuttack along with nine others across Orissa to address the educational needs of children of central government employees who are frequently transferred.
At present, there are 36 KVs in Orissa. While nine schools are in the project and defence sectors, the rest are in the civil sector.
The existing 36 Kendriya Vidyalayas are listed in http://kvsrobbs.org/DirectorKVs.html. As per that list the latest ones established in 2007 are in Rayagada, Parlakhemundi, Boudh, Malkangiri, Nawrangpur, Kandhamal, and Bhadrak. So the districts in Odisha that do not yet have Central Schools are:
- Deogarh
- Jajpur
- Kendrapada
- Nayagarh
- Nuapada
- Sonepur
I hope the new ones will cover these districts.
See our earlier articles on this topic at https://www.orissalinks.com/archives/556, https://www.orissalinks.com/archives/550 and https://www.orissalinks.com/archives/227.
April 9th, 2010
Following is an excerpt from a report in Business Standard.
… The HRD Ministry is set to revise its vocational education scheme under which the students will have the option to pursue vocational studies as an exclusive stream on par with arts, science and commerce.
The revised scheme, modelled on the pattern of vocational education in Australia and Germany, is expected to be announced next month.
"Students can study exclusively vocational education at Class-XI and XII. This will be an additional stream to the existing streams of science, arts and commerce," a senior Ministry official told PTI.
The focus of the revised vocational education stream will be industry collaboration at all stages, starting with designing of the courses, teaching and work experience in industry.
It will ensure employability of the students. Students can join any job or pursue further studies in professional courses like B.Tech after completing vocational courses.
… The vocational stream will offer a number of courses in areas like hospitality, automobile sector, paramedics, cooking, truck driving, manufacturing, graphics designing and animation, the official said.
Under vocational stream, the programmes will comprise 70 per cent of subject specific studies and 30 per cent general studies like English and communicative skills.
The revised scheme will be implemented across the country with 100 per cent Central assistance. The government has earmarked Rs 2,000 crore in the 11th Plan for this scheme. The Ministry is preparing a note for approval of Expenditure Finance Committee. Then it will go for Cabinet’s approval.
This is a great direction. When mainstream colleges start offering vocational courses and these programs have tie-up with industries that hire the graduates in apprentice positions with good prospects, the stigma associated with vocational programs in the mind of a typical middle class family in India would significantly reduce.
April 6th, 2010
The link is http://www.ugc.ac.in/pub/report/12.pdf. This was published in November 2008 with 500 printed copies. Its been recently put in the UGC website at number 12 in the page http://www.ugc.ac.in/pub/.
This 300 page document has all kinds of data on higher education in India and is a must read for anyone interested in higher education vis-a-vis India.
An Expressbuzz report by Sanjeev Patro tries to distill out some data with respect to Odisha from the above document. It is a good start and it made me look for the original document (Thanks), but I think a more careful analysis is needed.
March 1st, 2010
Following is an excerpt from a report in Business Standard on the 22 new polytechs.
… These polytechnics would come up in those districts which are not yet served by the government polytechnics. The districts include Boudh Gajapati, Nabarangpur, Bolangir, Kalahandi, Koraput, Kandhamal, Mayurbhanj and Balasore to name a few.
… It may be noted that 13 government engineering schools and polytechnics are already functioning in Orissa under the state industries department.
… A single patch of land spread over 10 acres has already been identified by the state government in each of the districts.
Out of Rs 12.3 crore sanctioned for each polytechnic, Rs eight crore will be spent on civil works and Rs 4.3 crore will be spent on equipment, machinery, furniture and learning resource material.
With the opening of these 22 polytechnics, every district in the state will have at least government polytechnic providing quality education.
Following is excerpt from a different report in Business Standard on the 91 new ITIs and 415 new Skill Development Centers (SDCs).
The Ministry of Labour and Employment of the Government of India has decided to set up 91 new ITIs (Industrial Training Institutes) and 415 Skill Development Centres (SDCs) in Orissa on the public-private partnership (PPP) mode.
While the Orissa government would provide basic infrastructural support for these ITIs and SDCs including free land with proper power, water and road connectivity, the Centre would provide Viability Gap Funding.
The proposed ITI s would have a strength of 250 trainees per shift running about 10 demand driven trades. An estimated Rs six crore would be spent towards infrastructural development on each of these ITI s.
The proposed SDCs would be smaller centres of vocational training with seating capacity of about 300 persons per shift per annum to meet the skill training needs of the locals.
About Rs 50 lakh would be invested on equipment and machineries for these SDCs.
Expressions of Interest would be invited from the training providers to operationalize these proposed ITI s and SDCs on the PPP mode.
… About 3-5 acres of land need to be identified for the establishment of ITI s at the unrepresented block headquarters while 500 sq m of land is needed for setting up the SDC at the gram panchayat headquarters.
Moreover, the Government of India has decided to upgrade 1396 government ITI s across the country on the PPP mode through an interest free loan of Rs 2.5 crore.
Nine ITI s in the state at Puri, Cuttack, Chhatrapur, Umerkote, Barbil, Dhenkanal, Barbil, Baripada, Baripada and Malkangiri are covered under this initiative.
February 26th, 2010
The advertisement http://www.cipet.gov.in/pdfs/advt.2010.pdf mentions that CIPET is upgrading its centers to High Learning Centers to impart B.Tech, M.Tech and Ph.D programs with exclusive R & D hubs ARSTPS & LARPM. (Note: I think LARPM was the first R & D hub to be created by CIPET and was mentioned in a Jan 2009 PIB report. But both were also mentioned in a May 2008 Economic Times article.)
As per http://www.cipet.gov.in/research.html:
Technology innovation through dedicated research work by a Core team has been the philosophy of CIPET, which led to the establishment of 02 R&D centres – Laboratory for Advance Research in polymeric Materials (LARPM) & Advance Research School for Technology & Product simulation (ARSTPS) at CIPET Bhubaneswar & Chennai respectively. …
The vision for these R&D Centres have been conceived with objectives of transforming CIPET as a Global research Centre on Polymeric Materials as well as a Resource centre for newer concept development & conversion of concept into reality by Product development on commercial scales. Technology transfer, creation of Intellectual Property (IP), knowledge base with validated documentation would be the key aspects of functioning of R&D entities.
The significance of LARPM & ARSTPS is evident from the fact that they will be chaired by Director General and functioning independently under the Technology & Business development department of Corporate Office. The targets for both R&D centres have been set to pursue the objectives in mission mode. The experienced & competent faculties have been drawn from the existing pool of CIPET along with newly inducted researchers.
Operating model of LARPM & ARSTPS would be influenced with 03 “Rs”- Relevance to industry needs, Result-oriented output, Resourceful base to operate as ‘Centre of excellence”. It is worth mentioning that LARPM has already been sanctioned 03 sponsored projects from Funding agencies of Govt. of India. Similarly, ARSTPS has already initiated industry sponsored projects for Automotive, Medical & Aerospace Industries.
The identified focus areas of LARPM & ARSTPS are as follows:
| |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| Biopolymers |
|
Innovative Product Design for Medical, Automobile, Aerospace and Packaging Industries |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| Polymer Composites & Nanocomposites |
|
Product and Tool Design Conceptualization (modeling, analysis, process optimization & simulation approach ) |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| Functional Plastics, Carbon nanotubes |
|
E- Manufacturing of Prototypes.
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Polymer Membranes, Conducting polymers
|
|
Reverse Engineering for metal and conventional
material substitution.
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Development & Characterization of Engg.
Polymers, Blends/Alloys |
|
– |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
The home page of LARPM is http://cipet.gov.in/cipetr&d/. As per http://cipet.gov.in/pdfs/research.pdf there are already 5 students pursuing Ph.D at LARPM. Following are concept drawings of their upcoming building.

The 2010-2011 admission ad shows the B.tech and M.tech programs that will be offered in 2010-2011. The program that will be offered at CIPET Bhubaneswar are:
- B.Tech in Plastics Engineering/Technology (Bhubaneswar, Ahmedabad, Chennai , Lucknow, Haldia – proposed)
- B.Tech in Manufacturing Engineering & Technology – proposed (Bhubaneswar, Ahmedabad, Chennai, Lucknow)
- M.Tech in Plastics Engineering/Technology (Bhubaneswar, Chennai , Lucknow, Hajipur)
- M.Tech in Polymer Nano Technology (LARPM – Bhubaneswar)
- M.Sc M.Tech in Material Science & Engineering (Bhubaneswar, Chennai, Lucknow).
The only program not listed to be offered at Bhubaneswar, but offered elsewhere, is
- M.Engg in CAD CAM (ARSTPS – Chennai)
Besides the above; all the 15 CIPET centers offer the following diplomas and PG Diplomas:
- Diploma in Plastic mould technology (3 yrs)
- Diploma in Plastics technology (3 yrs)
- PG Diploma in plastic mould design (1 yrs)
- PG Diploma in plastic processing & testing (1.5 yrs)
Finally, the Mancheswar branch of CIPET offers the following programs:
- ITI-Fitter, ITI-Electrician, ITI-IT&ESM and ITI-Welder
- and various short term courses and CAD/CAM courses.
From the above it looks like CIPET Chennai and Bhubaneswar are among the leaders. However neither Odisha nor Tamil Nadu have a NIPER. (The original NIPER is near Mohali and Chandigarh. As part of the 11th plan, new NIPERs were made in Hyderabad, Kolkata, Hajipur, Ahmedabad, Guwahati and Rae Bareli.) I hope Odisha pursues and gets one during the next five year plan.
February 20th, 2010
Following is an excerpt from the PIB http://pib.nic.in/release/release.asp?relid=56523.
Autonomous Institutions: There are seven existing autonomous institutions under Department of Biotechnology namely National Institute of Immunology (NII), New Delhi; Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics (CDFD), Hyderabad; National Centre for Cell Science (NCCS), Manesar; National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), New Delhi; Institute of Bioresource and Sustainable Development (IBSD), Imphal; Institute of Life Sciences (ILS), Bhubaneswar. Recently, Rajiv Gandhi Centre for Biotechnology (RGCB), Thiruvananthapuram has been taken over from Government of Kerala. These institutes have generated 382 publications, 24 patents granted/filed, 9 patents in pipeline and 13 technologies were developed.
Establishment of new breed of institutions in critical areas has been one of the major strategies of 11th plan. Cabinet has approved setting up of institutions namely Institute for Stem Cell Science and Regenerative Medicine, Bangalore; National Agri-food Biotechnology Institute with bioprocessing plant Cluster in Knowledge city at Mohali; Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI); Regional Centre for Biotechnology Training and Education under the auspices of the UNESCO, Faridabad and Institute of Biomedical Genomics in Kolkata and efforts are being made to establish institutions. In other proposed new institutions, National Institute of Animal Biotechnology, Hyderabad has been approved by EFC.
Regional biotechnology clusters , around the new institutions are being planned to promote innovation and discovery. These are the Translational Health Cluster at Faridabad, the Agrifood Cluster at Mohali and the Innovation Cluster at Bangaloore. Together, it is hoped that these will become the technology and innovation gateways of India.
December 31st, 2009
Following is an excerpt from a report in expressbuzz.com.
The Centre has sanctioned funds for establishment of Government polytechnics in 14 districts of the State.
Each of the institutes will receive a one time grant of Rs 12.30 crore from the Centre for infrastructure development while the State Government will take care of the recurring expenditure, including staff salary and administrative expenses.
The Government polytechnics will be located in districts having no such institutes.
Orissa has 13 technical institutes including three women polytechnics offering diploma courses in various trades. However, these institutes are limited to only nine districts and most of them are located in coastal region.
The new polytechnics will be opened in seven Naxal-affected districts of Malkangiri, Nabarangpur, Gajapati, Sambalpur, Jajpur, Nayagarh and Deogarh.
The other districts selected for the Centrally assisted technical institutes are Boudh, Nuapada, Kalahandi, Kendrapara, Jagatsinghpur, Puri and Sonepur.
Sites for the proposed polytechnics have been selected in respective district headquarters.
The Government will provide at least 10 acres of land for each of the polytechnics free of cost.
The new polytechnics will start functioning from the next academic session. …
According to a conservative estimate, each polytechnic will have at least 50 staff. The Government will take a decision on recruitment of staff on permanent or contractual basis.
The Government had already submitted a proposal to the Centre for financial assistance for opening Government polytechnics in the remaining seven districts.
October 29th, 2009
Update: The news item in Samaja.

Tathya writes about this. Following are some excerpts.
Central University of Orissa (CUO) will begin classes from June. … While CUO will have its campus in Koraput, to begin with a temporary campus near Bhubaneswar is being looked out to start classes from next Educational Year.
That is why Professor Banerjee has requested the Government of Orissa in Higher Education department to provide a rented accommodation.
Mr.Padhi has agreed to provide all out support for the institution.
Professor Banerjee is interested to make it a different institution and is inclined to start at least 30-35 departments in the newly carved out Centre of Learning.
However to start with the CUO will have 5 subjects and later it will go on including further, said sources.
… Those CUs, which has not identified land for the institution in the designated place, those can start it from the Capital City of the state, said sources.
So Professor Banerjee is busy in organizing things for facilitating classes from next June. Faculty hiring is the foremost in her mind and as she is eager to make it a top class university, the VC wants to rope in best of the talents from the country.
She is also interested to open Medical College in the University, but it will take time.
… Professor Baral of Arizona State University said only five of the 15 new central universities will have a medical college in the first phase (i.e.,during the 11th plan).
So the ability of the VC Professor Banerjee will be tested in whether she is able to get a medical and engineering college to the Central University of Orissa, feel the educationist.
Considering that the CUO is to be located in Koraput, in the most backward area, KBK, of India, Prof. Banerjee must do her best to make the right arguments at the earliest and get a medical and engineering college to this university, argued Professor Baral.
Page 522 of the document at http://planningcommission.nic.in/plans/planrel/fiveyr/11th/11_v3/11th_vol3.pdf given below shows that only 5 of the new central universities will have medical and engineering colleges in the first phase, I.e., during the 11th plan.

March 25th, 2009
In Section 8.44 (page 174) of Volume 1 (Inclusive Growth) of the 11th Five Year Plan, the following is mentioned.
The DAE has also initiated the process for establishment of the NISER at Bhubaneswar, at par with the IISER to undertake integrated five-year Masters’ courses and integrated M.Sc–Ph.D. programme in core and emerging branches of science to provide world-class education to students.
February 10th, 2009
Previous Posts



