From http://niser.iopb.res.in/careers/ the NISER pay is:
| Assistant Professor |
12,000-375-16,500 |
| Reader (F) |
14,300-400-18,300 |
| Associate Professor |
16,400-450-20,000 |
| Professor |
18,400-500-22,400 |
.. In addition to the basic salary, NISER faculty is entitled to allowances as admissible to Central Government Employees stationed at Bhubaneswar and to the DAE’s update allowance, which is currently Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 30,000 per year depending on the scale of pay. They will also receive other fringe benefits (like Relocation Grant, Reimbursement of telephone charges, financial support to attend national/international Conferences/Seminars/Workshops, etc.) which will be comparable to the best in the country.
From http://www.iiserkol.ac.in/career.html the IISER pay is:
1. Professor : Scale of pay : Rs 18,400 – 500 – 22,400
2. Associate Professor : Scale of pay : Rs 16,400 – 450 – 20,000
3. Assistant Professor : Scale of pay : Rs 12,000 – 420 – 18,300
including allowances as admissible to Central Government Employees in Kolkata.
… In addition to pay and allowances the faculty members may be provided with the following:
-
Reimbursement of telephone charges up to Rs 750 per month.
-
Rs 4000 per year as book grant.
-
Reimbursement of 75% of membership fee (restricted to Rs.5,000.00) of two international and two national professional bodies every year.
-
Financial support to attend national/international Conferences/Seminars/Workshops, etc.
-
Seed money for starting research laboratory.
I wonder if IISERs have something comparable to the DAE update allowance that NISER will pay. Otherwise that could be a selling point for NISER over the IISERs. Perhaps a knowledgeable reader can enlighten us on this aspect.
June 20th, 2008
The following was reported in bbiiser.blogspot.com.
Preamble:
Regional Centre for Biotechnology Training & Education under the auspices of UNESCO at Faridabad, Haryana, India will be an autonomus institution fully funded by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India.
The proposed Centre shall be a Category II Centre in terms of “Principles and Guidelines for the Establishment and Functioning of UNESCO Institutes and Centres”.
The emphasis is to support disciplinary & interdisciplinary education, training and research in biotechnology in order to produce skilled human resource to drive innovative research and development in the important gap areas.
As biotechnology sector is of global significance, the Centre would encourage global partnerships and co-operations.
Partnership with UNESCO would expand the opportunities to create world class education, training, research and will also facilitate global connectivity while preserving the regional & national focus of the institution.
Mission:
The Mission of the UNESCO Center is to create physical infrastructure in critical platform technologies and use it to support disciplinary & interdisciplinary education, training and research in biotechnology.
Vision:
To produce human resource tailored to drive innovation in biotechnology, particularly in areas of new opportunity and to fill talent gap in deficient areas.
Objectives:
(a) To produce human resource through education and training in a milieu of research and development for application of biotechnology for sustainable development towards building a strong biotech industry through regional and international co-operation.
(b) To establish desired infrastructure and Technology Platforms to support the activities of the centre.
(c) To establish a Technology Policy Development and Information Dissemination unit.
(d) To develop research programmes of a global quality through international partnerships to sustain world class education and training programmes.
(e) To enable periodic experimentation in design and implementation of biotechnology education and training and to be a source of new concepts and programmes, this can be assimilated by existing universities in India and the Region.
(f) To create a hub of biotechnology expertise in South Asian Association of Regional Co–operation (SAARC) region, and more generally in the Asian region and to address human resource needs.
(g) Promotion and strengthening of South-South & South-North co-operations around issues relevant to biotech education, training, innovation, commercialization and trade.
(h) Promotion of a network of satellite centers in the region.
Focus:
The primary focus of the Centre is to provide high quality human resource in disciplinary and interdisciplinary areas.
The Centre would provide outstanding disciplinary/interdisciplinary short term training programmes which will include Science & Technology training for physicians, biologists and engineers by networking through local hospitals/ medical & engineering schools etc.
In addition, short term training programmes in platform technologies will be conducted for skill development in existing personnel.
Specialized domain specific programmes will also be created in new emerging areas.
The Centre will offer specialized master’s degree courses, unique Ph.D. programmes, domain specific training programmes, high quality research and development in the specific areas.
The Centre will have a centralized Science & Technology platform and Technology Management & Enterprise Development Unit.
India is poised to be the hub for biotechnology in the coming decade; therefore the Centre would provide a window for showcasing Indian competence in global market for economic gains. Policy harmonization on trade and regulation will also be facilitated as a part of this effort.
Programmes Details:
1. As Educational Hub:
(a) Special Master’s Degree courses:
The Centre will offer special Master’s Degree courses of two years duration in the following areas:
v Biosciences,
v Bioengineering,
v Drug Discovery Science,
v Translational and Clinical Health Science,
v Molecular Crop Breeding,
v Regulatory Affairs,
v Biomedical Quality Systems and Product Development,
v Infectious Disease Biology,
v Bioinformatics etc.
It will also help to enrich the existing Master’s in Biotechnology programmes and cater to the needs of the Asian region and members countries.
(b) Unique PhD Programmes:
The Centre will offer unique M. Tech.-PhD programme in Biomedical engineering,
Integrated M.Sc-PhD programme in Medical bioscience and drug discovery,
PhD in
v Molecular Crop Biotechnology,
v Nano-biology,
v Synthetic Biology related to Health, Plants and Energy
v Interdisciplinary PhD programme (on the lines of MIT Harvard HST programme).
The Ph.D. programmes of the UNESCO Center will be open to Indians as well as students from the member countries and Asian region. A few fellowships will be available to students opting for these programmes on a competitive basis.
The students will have access to:
v Disciplinary & Interdisciplinary, Tech Strong & Industry Linked Environment
v Expertise of Research Centers of Excellence: Institutional, Regional & Global
v Multicultural & Global Environment
v Learning Skills of International Standard
v Overseas Mentors
2. Training Programmes:
(a) The training programme will be unique to the Centre with the goal to arrange/organize personalized or user-friendly opportunities for career development. Structured training courses for physicians and engineers (intending to enter biology), science managers and industry personnel in specific areas where they require skill enhancement will have emphasis.
(b) The Centre’s Technology Incubator & Business Development Unit will be open to industry for enhancing their skills in specific areas through structured training courses for career opportunities/ advancements in the areas like:
v IPR,
v Technology Transfer,
v Bio-enterprise/ Management in Biotechnology,
v Platform Technologies,
v Regulatory Procedures,
v Biosafety,
v Bioethics,
v Process Development and Up-scaling,
v Preclinical Toxicity and Clinical Trials,
v Good Manufacturing Practices & Good Laboratory Practices,
v Biostatistics,
v Epidemiology etc.
(c) Specialized Domain Specific Training Programmes will also be designed for people from basic sciences in:
v Nanotechnology,
v Implants and Devices,
v Vaccine Development,
v Stem Cell Biology etc.
3. Research:
The research emphasis will be in the areas like:
v Nano-biology,
v Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering,
v Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacogenomics,
v Molecular Metabolism and Nutrition,
v Bone & Cartilage Biology,
v High Throughput Clinical Genomics,
v Diabetes,
v Infection Science Microbiology & Vaccinology,
v Molecular Diagnostics,
v Crop Breeding etc.
Post-doctoral Programmes:
v Re-entry Grant to Talented Scientists working abroad.
v Young Investigator Awards to work for 3-5yrs after PhD
PROGRAMMES AND SUB-PROGRAMMES AT UNESCO CENTRE
Programmes:
v Biological Sciences
Sub-programmes:
F Immunology
F Molecular biology
F Molecular biophysics
F Structural biology
F Molecular Cell biology
F Bioinformatics
F Bio-organic Chemistry
v Pharmaceutical Biotechnology
v Bioengineering & Material Science
v Industrial Biotechnology
v Molecular Crop breeding
v Molecular Medicine – I (Infectious diseases)
v Molecular Medicine – II (chronic diseases)
v Applied health science Division
v GMP Units
F Vaccine production
F Cell and tissue based therapies etc.
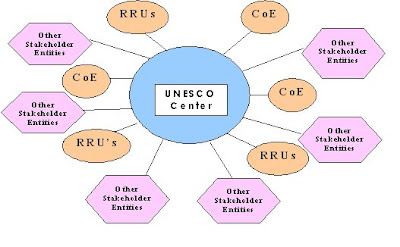
UNESCO Center
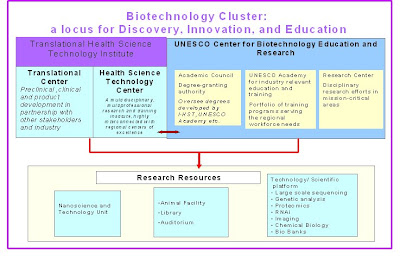
The research carried out at the Centre will be supported by various programmes and collaborations at the national and global levels like Translational Health Science and Technology Institute, Autonomus Research & Development Institutions, Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), Medical Schools, Biotechnology Centres at regional and international level etc. as per the guidelines to be formulated by the Board of Governors. It will consider supporting Research Resource Units (RRU’s) and Centre for Excellence (CoE) with Indian or Regional institutes in strategic areas where partnership is critical for collaborative research. It will also provide access to technology platforms to scientists from other institutes and industry. The extramural collaborations will have provisions for adjunct professorships, visiting professor programmes and scientist exchange programmes etc.
OTHER ACTIVITIES OF THE UNESCO CENTER:
The Centre will have the provisions for Visiting Professorship for Indian Nationals & International Scientists, Adjunct Professorship, Stanford-India Bio-design Programme, Re-entry Grant and Young Investigator Awards.
CENTRALIZED SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY PLATFORM:
The platform technologies will be available in the areas of
v Large Scale Sequencing,
v Genetic Analysis,
v Proteomics,
v RNAi,
v Imaging,
v Chemical Biology,
v Bio Bank etc.
This centralized science and technology platform is expected to provide service to the scientists of the research divisions of health science & technology, and provide support to the training activities of the UNESCO Centre and other research institutes in the country.
In due course it will develop liaison with national and international databases and consortia in order to contribute to global scientific resources.
TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT AND ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT UNIT:
The infrastructure of this unit will have ready to use laboratory space for extramural scientists for innovative & translational research projects. In partnership with the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), GMP units for cell based therapy and vaccine will be made. The faculty of this unit will have skills in technology transfer, IP managements, finance and enterprise creation.
Organization Structure:
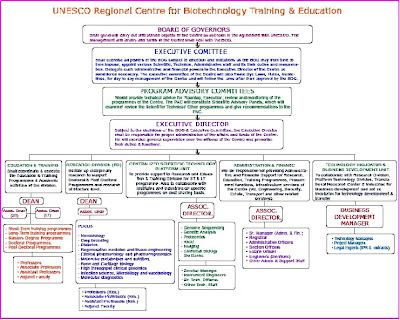
Administration & Finance Unit:
This unit will provide administrative, financial, engineering and other support services to the Centre. Services like security, housekeeping, office attendants, operation & maintenance of services will be outsourced to firms who provide manpower on contract.
Location:
The Centre will be situated in a picturesque location in Faridabad about 25 km from New Delhi (40 minute drive) in the academic and research ambience of the Life Sciences Cluster and an adjacent R & D Centre of another Ministry of the Government of India to be set up in the near future.
The site is also close to other renowned institutions like the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS); Indian Institute of Technology (IIT); International Centre for Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology (ICGEB); Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU); National Institute of Immunology (NII); National Brain Research Centre (NBRC), with whom the centre is likely to establish network and collaborative programmes, are also situated within 20-30km radius of the centre.
v Meeting with National Experts was held on May 18, 2007.
v An interactive meeting on the UNESCO Centre was jointly organized by DBT and UNESCO on June 18-19, 2007 at New Delhi to discuss the focus, activities, organizational structure and linkages of the proposed Centre.
The meeting was attended by eminent scientists, educationists, policy makers and stakeholders from the members countries, counties of the South East Asian Region as well as by representatives from the industries as well.
The experts nominated by UNESCO provided insights into global partnerships and benefit- sharing especially with regard to guest/visiting faculty, fellowships and participation of member countries.
Meeting held on June 18-19, 2007 at New Delhi
v A meeting was organized with Boston University delegation, USA, led by its President – Prof. Robert Brown, towards developing partnerships for education, training and research with the UNESCO Regional Centre for Biotechnology Training & Education and Translational Health Science & Technology Institute (THSTI) in New Delhi on September 25, 2007.
Current Status:
v An Interim Advisory Committee (IAC) has been constituted to provide Scientific and Academic directions.
v A Management Cell has been created at NII, New Delhi to address the interim issues
v Initiatives for collaborations/partnerships with international institutes/universities have been started. MoUs have been signed with Stanford and Boston University.
v Actions have been initiated for revised Cabinet approval, Legislative Bill for Act of Parliament, constitution of various committees, web-design, building construction etc.
June 18th, 2008
Following is from http://www.ugc.ac.in/notices/proposals6-5-08.pdf.
1. Krupajal Engineering College, Pubasasan, Kausalya Ganga, Bhubaneshwar – 2, Orissa.
F. 9-17/2007- U.3 (A); dated 15th March, 2007; withdrawn. Fresh proposal received under De-Novo Category. No. F.9-27/2008 dt. 15.4.08
The Institute has withdrawan the proposal under General Category. No. F. 35-7/2007 (CPP-I) Proposal for De-Novo Category is under process.
2. College of Engineering, Bhubaneswar, Under Nabadigant, Educational Trust, Plot No. 1, Sector – 3, Chandaka Nucleus
Industrial Complex, Patia, Bhubaneswar – 751 024, Orissa. De-novo
F.9-30/2007-U.3 (A) dated 15th May, 2007
The Institute has been asked to comply with the deficiencies vide UGC Letter No. F. 35-3/2007 (CPPI) dated 27th August, 2007
3. Asian School of Business Management Bhubaneswar, Orissa. De-novo
F.9-45/2007-U.3 (A) dated 18th September, 2007
Letter for State Govt.’s Views has sent. The file is in process vide UGC File No. F. 35-5/2007 (CPP-I)
4. Vidya Bharti University, Gunupur, Distt. Rayagarha, Orissa
F.9-60/2007-U.3(A) dated 28.11.2007
The Institute has sent the compliance to this office letter dt 28.1.08 and the file is under process. F. 35-6/2007 (CPP-I)
5. Koustav Institute of Self Domain Patia, Bhubaneswar, Orissa. (DE-NOVO)
F. 9-68/2007- U.3(A) dated 9th January, 2008
Information has been called in checklist proforma vide UGC Letter F. 35-1/2008 (CPP-I) dt. 4.2.2008.
6. HI-TECH University, Plot No. A-170, Saheed Nagar, Bhubaneswar, Orissa.
F. 9-4/2008-U.3(A) dated 15th January, 2008
Information has been called in checklist proforma vide UGC Letter F. 35-2/2008 (CPP-I) dt. 6.2.2008.
7. C.V. Raman University, Bhubaneswar, Orissa.
F. 9-67/2007- U.3(A) dated 9th January, 2008
The Institute has been asked to comply with the deficiencies vide letter dt. 30.4.08 F. 35-4/2008 (CPP-I)
June 17th, 2008
(Update: New Indian Express also reports on it.)
Following is from a report in Pioneer.
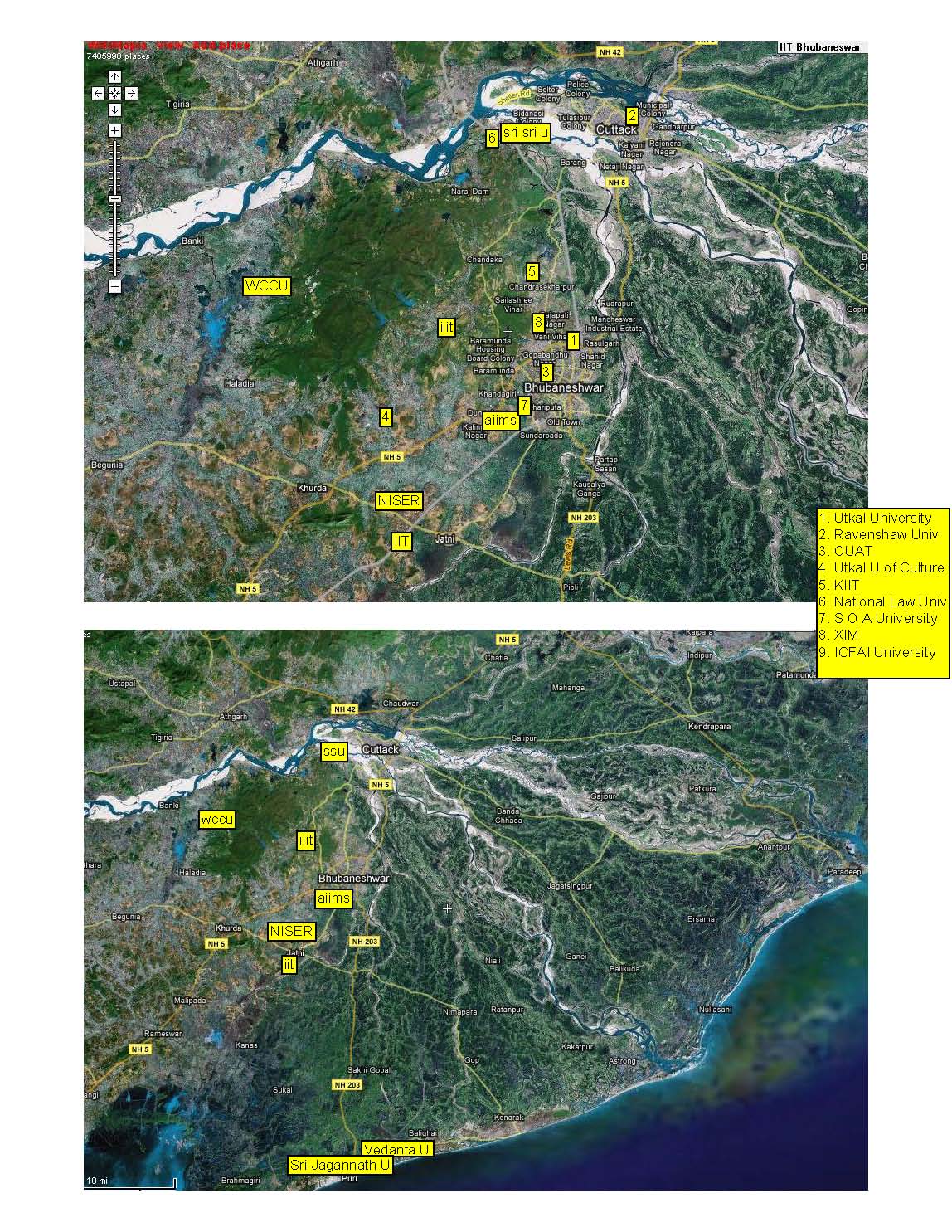
Friends and well-wishers have developed a comprehensive website for IIT Bhubaneswar. The website, http://iitbbsr.net, talks about advantages of IIT Bhubaneswar over other new IITs. It includes a section of frequently asked questions (FAQs).
Among the advantages of IIT Bhubaneswar is the fact that the first year classes will be held at IIT Kharagpur. And the students will be living with IIT Kharagpur students in the same hostels and taking classes taught by the faculty of the institute. Thus, these students will have a firsthand experience of an established IIT and will be able to bring the culture and traditions to IIT Bhubaneswar.
The other advantages of IIT Bhubaneswar are that it will be located in a well-connected metropolitan area with a population of 16.36 lakh. This is not too small to lack amenities and not too big to have the problems of big cities such as high crime rate, traffic congestion, power cuts, pollution, water scarcity, and mega slums.
Among the amenities, the IIT will be located right next to the lush green Chandaka-Dampara Elephant Sanctuary and close to the banks of the river Mahanadi. The green environment will provide the IITians plenty of opportunities to interact with the nature and recharge their brains.
At the same time, the students will be close to the malls, a water park, bookshops, museums and other urban facilities of Bhubaneswar. In terms of connectivity, Bhubaneswar is well-linked to the rest of the country by rail (from Amritsar, Hardwar, Goa and Cochin to Guwahati and Dibrugarh), road and air (Indian, Jetlite, Indigo, Kingfisher and Deccan).
But the main advantage of IIT Bhubaneswar will be that it will be driven to excellence by competition and collaboration with other national and premium institutes. The presence of NISER (National institute of Science Education and Research, which is at par with IISER but funded by DAE, proposed world-class Central University and the Rs12,000-crore Vedanta University will be advantageous to them.
It will provide the IITians additional research and management opportunities at XIM (Xaviers institute of Management), AIIMS-like institute, National Law University, Institute of Physics, Institute of Life Sciences, Institute of Minerals and Materials Technology, Regional Medical Research Centre, Regional Plant Resources Centre, CIFA and CRRI.
In addition, Bhubaneswar houses the country’s major software companies, including Infosys, WIPRO, TCS and Satyam, and is the State’s hub in terms of investment. Finally, the social life and career of the IITians will be complimented by the presence of 30-plus other engineering colleges, seven universities (Utkal, OUAT, Culture, Ravenshaw, KIIT, SOA and Sri Jagannath) and two other upcoming universities (ICFAI and Sri Sri), in the area.
With all these advantages, and the State Government’s extraordinary support, whereby it plans to give 1,000 acres of land to IIT Bhubaneswar, much more than the 500-600 acres that the Union Ministry of Human Resource Development has suggested, IIT Bhubaneswar is destined to be among the top IITs of the country, feel educationists.
June 17th, 2008