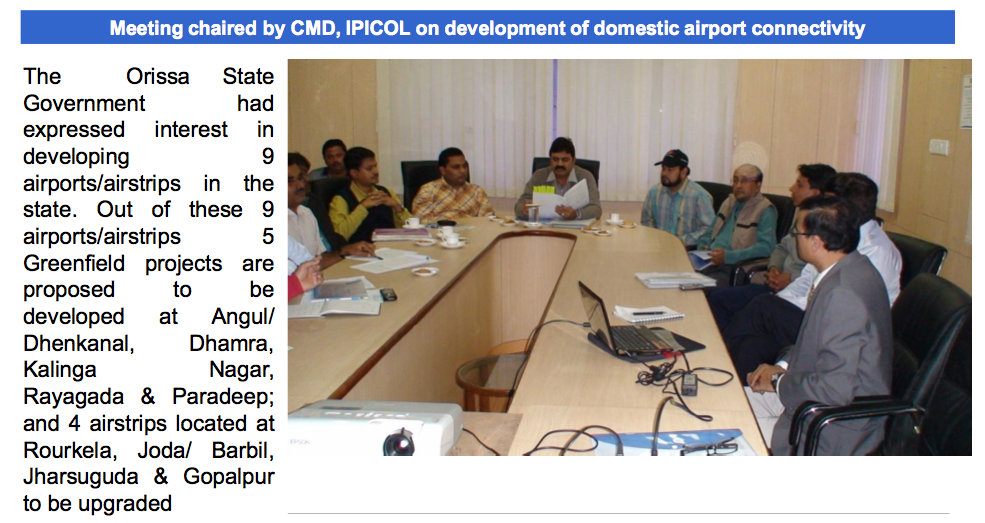
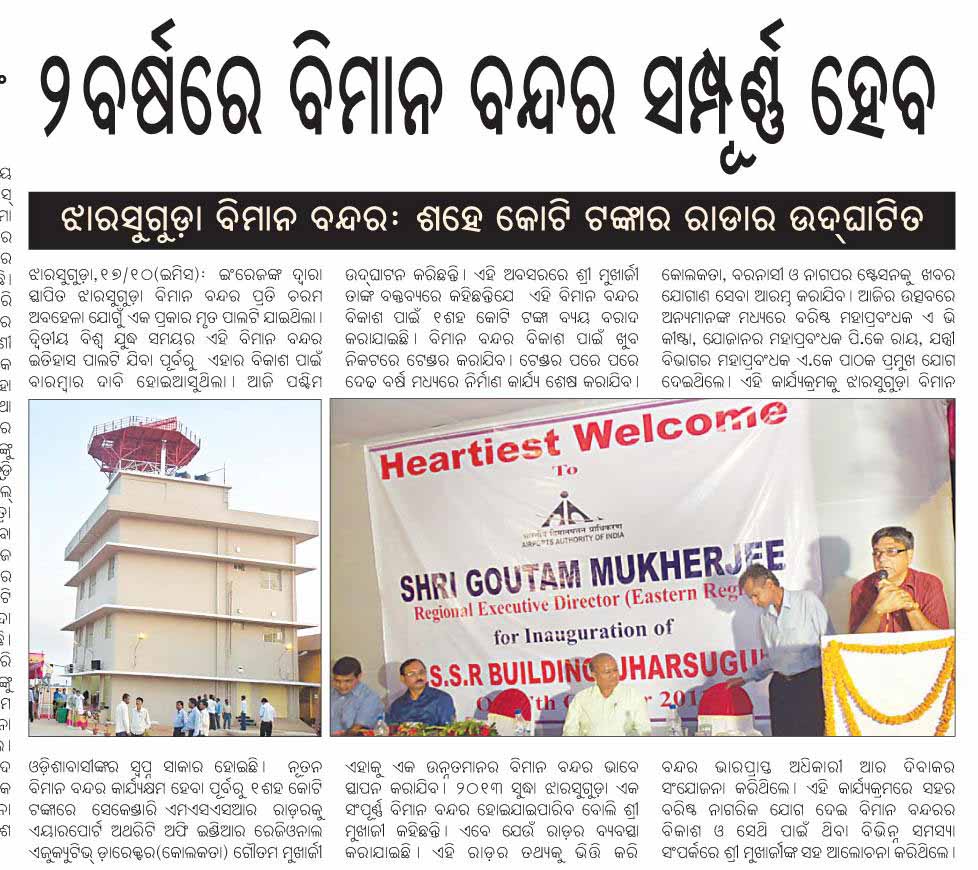
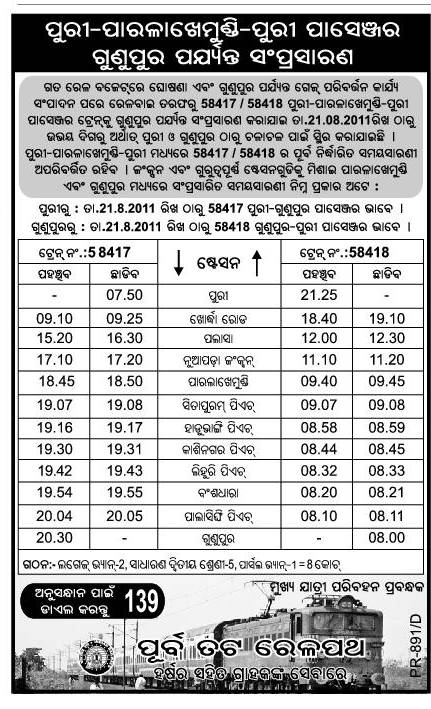
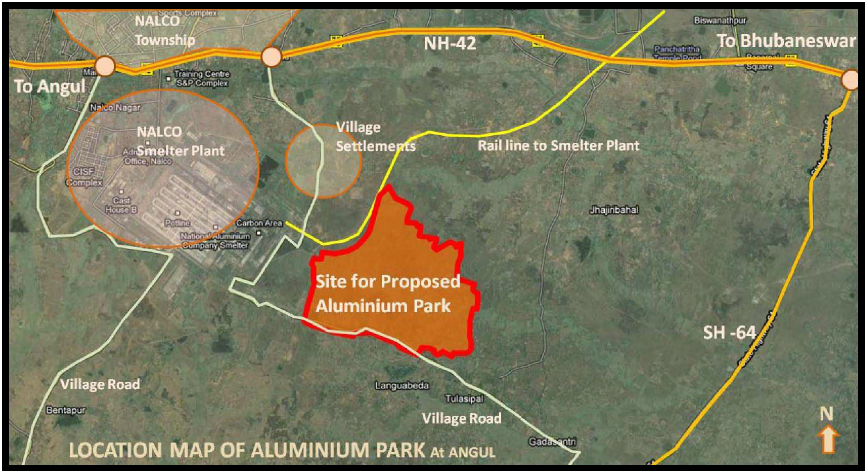
The draft approach paper to the Twelfth plan is at http://planningcommission.gov.in/plans/planrel/12appdrft/appraoch_12plan.pdf.
Following are some excerpts.
Page 6: 1.12 One critical parameter to examine the degree of inclusiveness is to see what has happened to the real farm wages in the rural areas. This is because the largest number of poor, primarily landless workers, is in rural areas and the majority of them still rely on farm work for their livelihood. It is comforting to see that during the period 2007 to 2010 (calendar years), the average real wage rates have increased by 16 percent at an all India level. The growth was the fastest in Andhra Pradesh (42%) and Orissa (33%). Even in states like Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, real farm wages went up by 19 and 20 percent respectively, over the three year period.
Page 50: 3.33 Access to power has been particularly poor in rural habitations and the Rajiv Gandhi Grameen Vidyutikaran Yojana RGGVY was devised to remedy this problem by providing connections to all villages and free connections to BPL families. There are, however, still a large number of habitations left uncovered and a very large population that has no connectivity. It is desirable to try and universalize access of power during the Twelfth Plan and this requires dealing with the large backlog in the States of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Orissa and Assam and some of the other North East States. However for effective universal access the RGGVY programme has to be restructured. Connectivity by itself is only part of the problem, since in many States there is also a real shortage of power. Besides RGGVY focuses only on household supply and does not address the need for providing electricity for agriculture, which needs three phase supply. This in turn requires strengthening of the rural network, and not just last mile connectivity to households, which is what RGGVY covers.
Page 56: 4.7 A master plan for 18,637 kilometres of expressways, with new alignments for both passenger and freight movements in high traffic density corridors based on “access control toll” needs to be taken up. These roads will be either 4 or 6 lane. The proposed National Expressway Authority of India is expected to take the initiatives for both land acquisition and to get the work executed under BOT mode.
Page 120: 9.19 District Hospitals need to be greatly strengthened in terms of both equipment and staffing for a wide range of secondary care services and also some tertiary level services. They should actually be viewed as District Knowledge Centres for training a broad array of health workers including nurses, midâ€level health workers (e.g. Bachelor of Rural Health Care or Bachelor of Primary Health Practice) Paramedics and other public health and health management professionals. New medical and nursing colleges should preferably be linked to district hospitals in underserved states and districts, ensuring that districts with a population of 25 lakhs and above are prioritized for establishment of such colleges if they presently lack them. New programmes for developing midâ€level health workers (such as Bachelor of Rural Health Care/Bachelor of Primary Health Practice) and nurseâ€practitioners which have been ntroduced in some States must be similarly linked to District Hospitals and their attached District Knowledge Centres.
Page 120: 9.25 Lack of human resources is as responsible for inadequate provision of health services as lack of physical infrastructure, especially in rural areas. According to Rural Health Statistics (RHS), 2,010, there is shortage of 2,433 doctors at PHCs (10.27 per cent of the required number); 11,361 specialists at CHCs (62.6 per cent of the required number); and 13,683 nurses at PHCs and CHCs combined (i.e., 24.69 per cent of the required number). In addition 7,655 Pharmacists and 14,225 Laboratory Technicians are needed at PHCs &CHCs (27.13 per cent and 50.42 per cent of the required number) in the country. These numbers are based on the 2001 Census.
9.26 The status of Human Resources for Health (HRH) has improved during the 11th Five year plan period, however much more needs to be done. The density of doctors in India is 0.6 per 1,000 and that of nurses and midwives is 1.30 per 1,000, representing jointly 1.9 health workers per 1,000. While no norms for Health Human Resource have been set for the country, if one takes a threshold of 2.5 health workers (including midwives, nurses, and doctors) per 1,000 population, there is shortage of health workers. Furthermore, because of a skewed distribution of all cadres of health workers, the vulnerable populations in rural, tribal and hilly areas continue to be extremely underserved.
9.27 The Twelfth Plan must therefore ensure a sizeable expansion in teaching institutions for doctors, nurses and paramedics. Only 193 districts of a total of 640 have a medical college – the remaining 447 districts do not have any medical colleges. Further, the existing teaching capacity for creating paramedical professionals is grossly inadequate. Against 335 medical colleges, there are 319 ANM training schools, 49 Health and Family Welfare Training Schools and only 34 LHV training schools. To fill the gap in training needs of paramedical professionals, the Twelfth Plan proposes to develop each of the District Hospitals (635) into knowledge centres, and CHCs (4535) into training institutions.
Page 131: 10.20 There must be a strategic shift from mere expansion to improvement in quality higher education. For this, the focus should be not only on larger enrolment, but also on the quality of the expansion. During the Twelfthâ€Plan period, an additional enrolment of 10 million could be targeted in higher education equivalent to 3 million additional seats for each age cohort entering the higher education system. This would significantly increase the GER bringing it broadly in line with the global average.
10.21 A holistic and balanced expansion approach is needed to target underâ€represented sections of society. Thrust should be on consolidating and improving the capacity and quality of the existing institutions. New institutions may be set up to bridge regional imbalances and disparities across disciplines and to address special economic, social and technological needs of the country. Further, traditional education should be supplemented with skillâ€based studies and institutional differentiation should be encouraged so that institutions grow along their own growth trajectories without being clones of each other. Open and distance education methods could be deployed to augment capacity optimally. In addition, the concept of Meta University aimed at collaborative and multiâ€disciplinary learning that redefines knowledgeâ€creation and knowledgeâ€sharing in the twentyâ€first century, could also be explored.
10.22 There is an urgent need to step up both public and private investment in higher education (including technical), and increase in the efficiency of its utilization. About 18 per cent of all government education spending or about 1.12 percentage of GDP is spent on higher education today. This should be raised to 25 percent and 1.5 per cent respectively. An increase of 0.38 per cent of GDP means an additional allocation of about Rs.25, 000 crore to higher education for the Centre and the States taken together.
10.23 State universities and their affiliated colleges that account for more than 90 percent of the enrolment suffer from severe fund constraints and poor governance leading to poor quality. Strategic Centralâ€funding based on State higher education plans should be leveraged to stimulate more state funding linked to academic and governance reforms which may include normâ€based funding for State universities and colleges. Allocation of operating budget should be based on objective norms and new investments based on competitive grants and performance contracts. Institutions should be encouraged to raise their own funds through various legitimate means. Reasonable tuition fees in higher education need to be supplemented with appropriate publiclyâ€funded financial aid. The scale and reach of scholarship schemes and student loans need to be enhanced. Government guarantees for student loans could be considered. The central principle should be that no student who is eligible to be admitted should be deprived of higher education for financial reasons.
Encouraging Private Participation
10.26 Private sector growth in higher education (including technical) should be facilitated and innovative Publicâ€Private Partnerships (PPP) should be explored and developed in the Twelfth†Plan. Private higher education accounts for about fourâ€fifths of enrolment in professional higher education and oneâ€third overall. This growth trend is likely to continue in the Twelfth Plan. Currently, this growth is restricted to specific areas and there are concerns about quality and use of unfair practices. A clear policy is therefore required to manage private education and a statutory and transparent framework needs to be established for its operation for driving private growth further in a legitimate and balanced manner. The “notâ€forâ€profit” tag in higher education sector should, perhaps, be reâ€examined in a more pragmatic manner so as to ensure quality without losing focus on expansion and equity. Deserving private institutions could benefit with access to public funds in the form of loans, financial aid for students and competitive funding for research.
Research Culture and Faculty Issues
10.27 We must bring back the ‘lost’ research culture of Indian Universities so as to create new knowledge and improve teaching standards. This would require more funding for university†based research and funding policies that create right incentives for quality research and promote collaboration among institutions. Related to this is the issue of faculty shortages which can be tackled through innovative ways such as technologyâ€enabled learning and collaborative information and communication technologies (ICT). A complete overhaul of the Academic Staff Colleges that are used to provide refresher courses for teachers is also necessary. Initiatives to improve the quality and availability of teachers in higher education need to be launched in a mission mode. With improvements in life expectancy, a growing pool of retired and elderly people is now available in the country. They have potential to enrich teachingâ€learning experience and act as social capital for the society. It is possible to tap and convert their valuable acquired expertise into useful codified knowledge through a special Ph.D. programme for senior citizens facilitated by liberal entry requirements.
Page 134: 10.30 While most of our universities and colleges are required to build human resources to reach desired levels of competence, we also need to go beyond this to ensure that the country has several institutions of higher education that strive to achieve excellence in both teaching and research. The latter needs significantly large resources and, also much greater institutional autonomy and approval incentive structures. Realistically, India should aim to have at least a few universities in the global topâ€league. To achieve this as quickly as possible, the country should act on two fronts. It should create new topâ€end universities and also upgrade very good ones. A few new Innovation Universities could be established urgently, and several universities and institutions could be converted or upgraded by creating centres of excellence within the University, building on their existing strength. At the core of achieving excellence, is ability of institutions to attract and retain high quality faculty from across the world. This not only requires providing them with competitive salaries but also ensuring a challenging work environment and a lot of flexibility. The Twelfth Plan should attempt to operationalize these objectives.
10.31 In addition, the idea of creating large education hubs on fallow lands at four or five locations in the country, anchored by large public sector enterprises (possibly with participation by the private sector) and funded through their allocations for corporate social responsibility needs to be explored. These could be models for industryâ€institute interface and would ensure local and regional development of areas where these are located.
10.32 Higher education is an increasingly global enterprise; hence Indian institutions should embrace internationalization that could provide them with new opportunities. Country’s rationale for internationalization would be to enhance its soft power, improve standards of domestic provision and produce graduates with international competencies and skills. This can best be achieved by having more and innovative partnerships. Given the historical advantage in higher education (particularly among emerging market economies) the wide spread use of English language and low cost living, India can potently become a global hub for higher education. We need to provide greater autonomy to our Centres of excellence to enter into collaborative partnership with the best universities abroad.
Page 138: Backward, Border and Remote Areas
11.11 Special emphasis must be given in the XIIth Plan for connecting to areas where connectivity is poor, which is one of several reasons why they are unable to become active participants in the growth process. These areas include the mountainous Himalayan region, the underâ€developed pockets in Central and Eastern India, the islands territories and some regions in the North East. A large number of districts (often characterised by forested areas with tribal population) in the States of Andhra Pradesh, Orissa, Chattisgarh, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh have experienced much less development than the overall development of the States within which they are located. They are also affected by Left Wing Extremism. Some of these less developed regions are spread across state boundaries, such as Bundelkand, which extends across Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. In other instances these are pockets within a state that are historically fraught with difficult conditions. Notable amongst them are the Vidharbha region of Maharashtra; the Kalahandi, Bolangir and Koraput (KBK) region in Orissa and most of the tribal belt in Central and Eastern India.
11.12 To deal with the legitimate aspirations of the people of these neglected regions the overall growth strategy must have a component of regional development. This will require interâ€state cooperation and strengthening the pace of development of interâ€state and intra†state connectivity of tribal and other isolated communities through forests and difficult terrain. It will need better governance and deeper involvement of local people in the development process. Skill development and employment opportunities must be an important component of this strategy. The XIIth Plan will identify such areas for continued and enhanced development.
11.13 The development of physical infrastructure coupled with opportunities for education and skill development can generate significant improvements in livelihood and incomes and result in better sharing of the fruits of economic growth with these remote areas.
Plan within a Plan
11.14 A special effort is needed in the Twelfth Plan to create a Plan within a Plan. There are already programmes such as the Backward Regions Grant Fund (BRGF), Border Area Development Programme (BADP), Hill Area Development Programme (HADP), the Kalahandi, Bolangir and Koraput (KBK) Plan, the Bihar Special Plan, the Bundelkhand Special Package, and most recently, the Integrated Action Plan (IAP) for Left Wing Extremism (LWE) affected districts. The XIIth Plan should create a greater coherence among all these Special Plans.
Page 154: 13.16 Finally, the institutional concepts which were initiated in earlier Five Year Plans, like the Inter University Centres and Interâ€Institutional Centres for enhancing research and educational linkages for Universities, are to be expanded further to cover many other interâ€disciplinary research areas such as Earth System Science, life sciences, Computational Science, Cognitive Science etc., during the Twelfth Plan to bring about functional connectivity across universities and domain institutions. This would also overcome regional disparities in the quality of education/research.
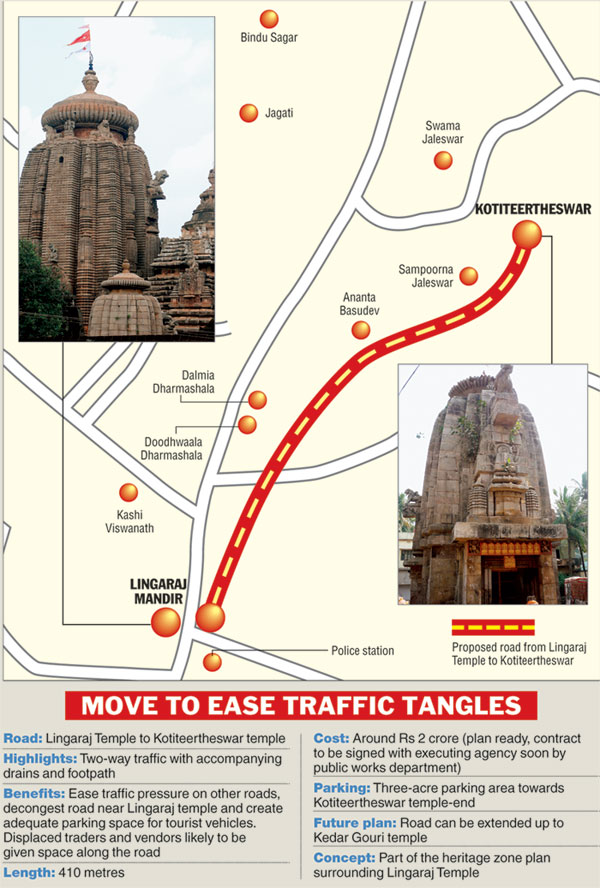

 In the 83 SRE districts all the expenses incurred on security in these districts are reimbursed by the MHA. These districts were identified
In the 83 SRE districts all the expenses incurred on security in these districts are reimbursed by the MHA. These districts were identified